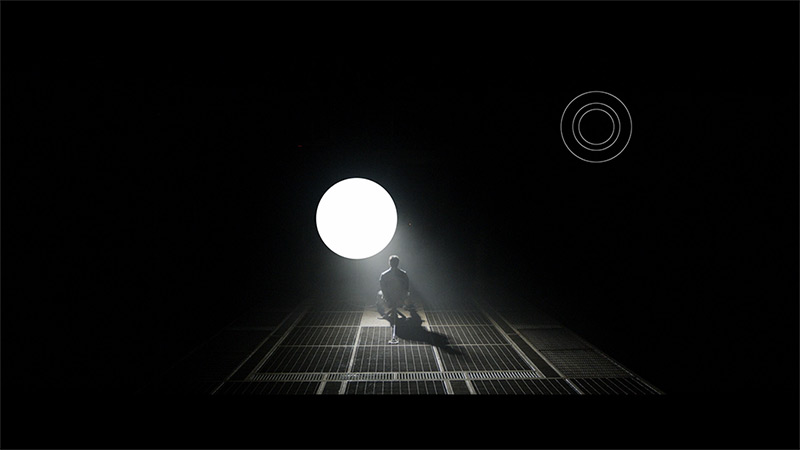
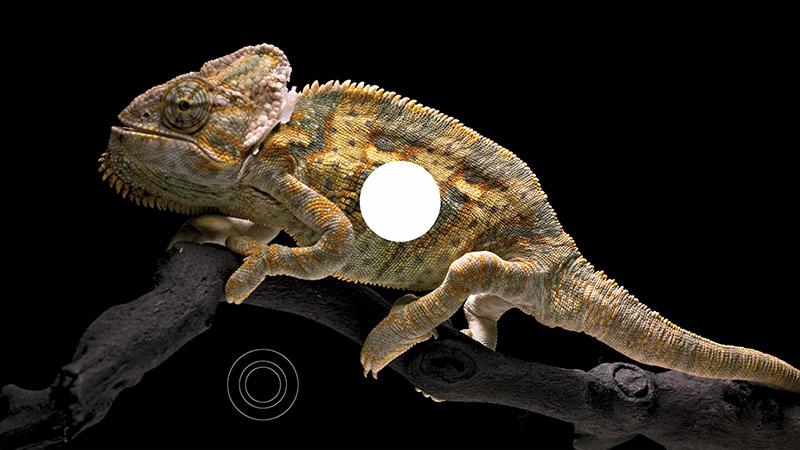
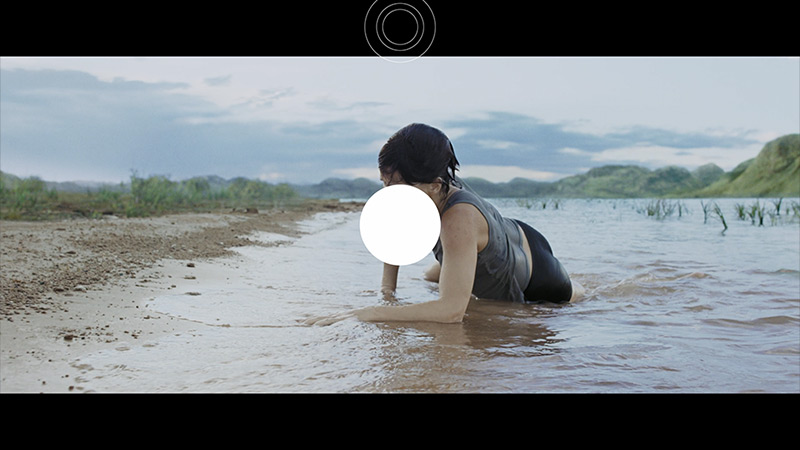
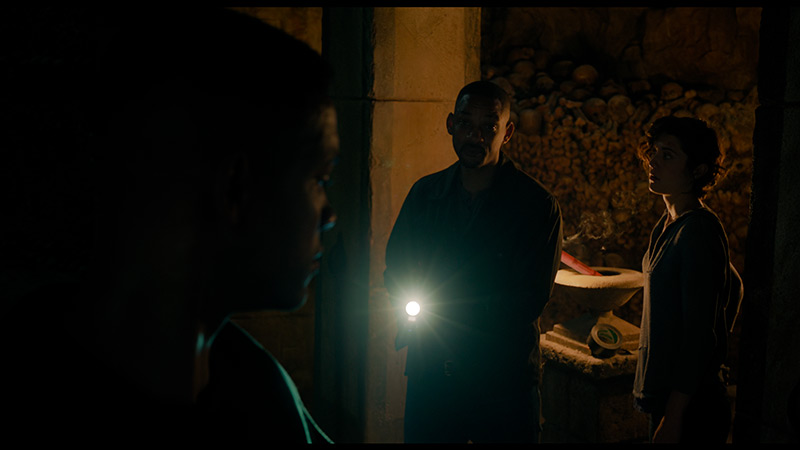
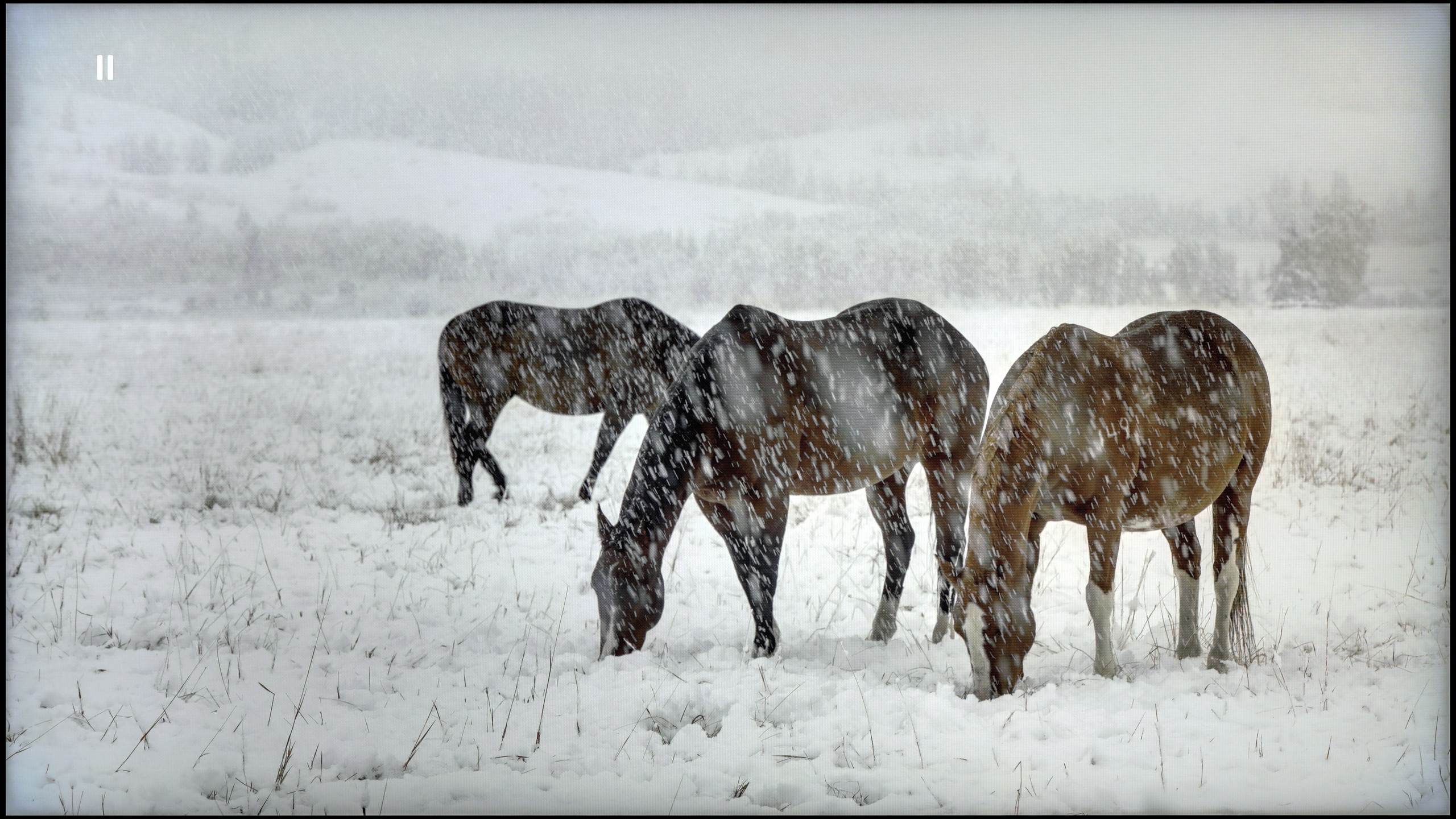
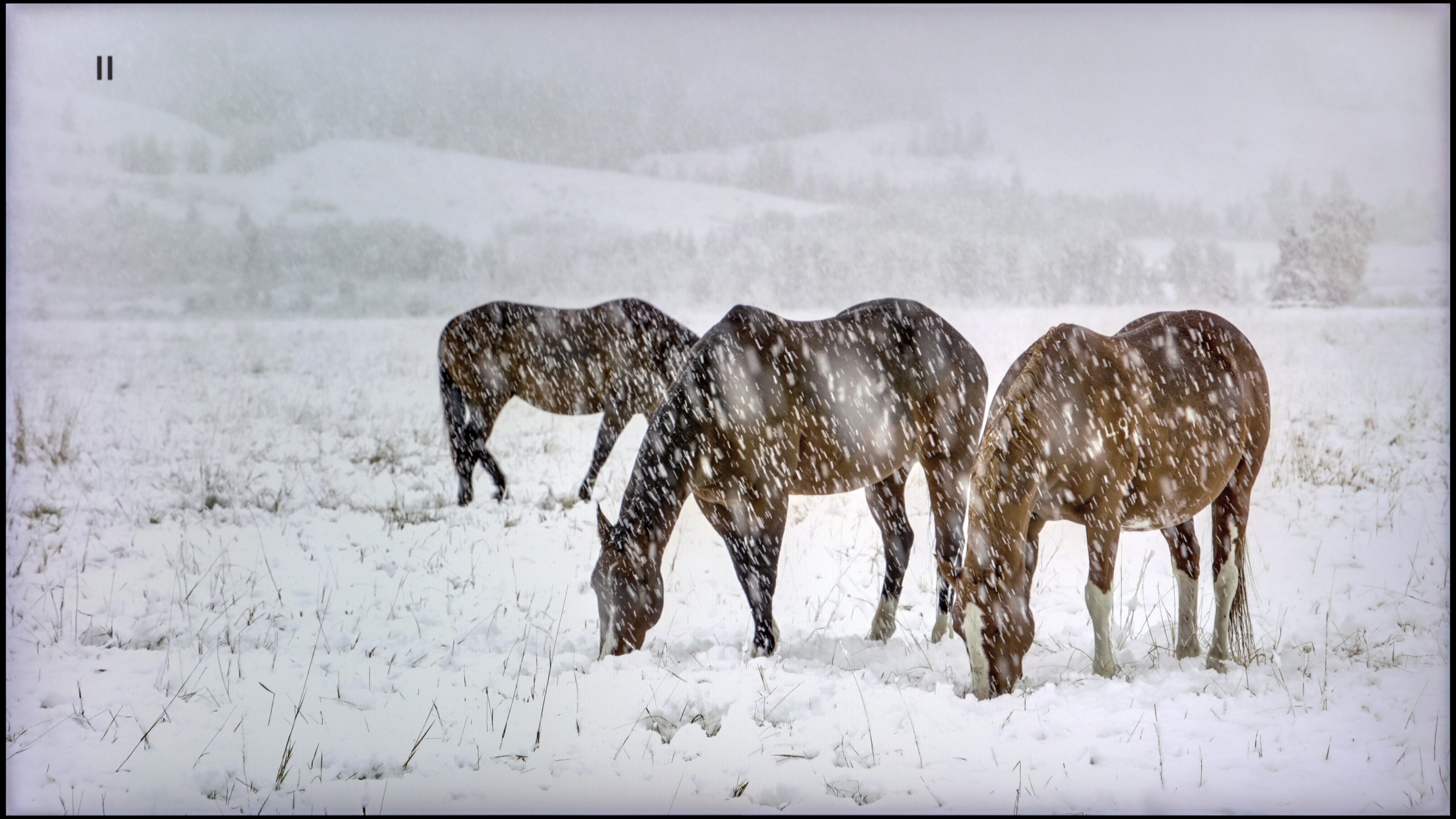
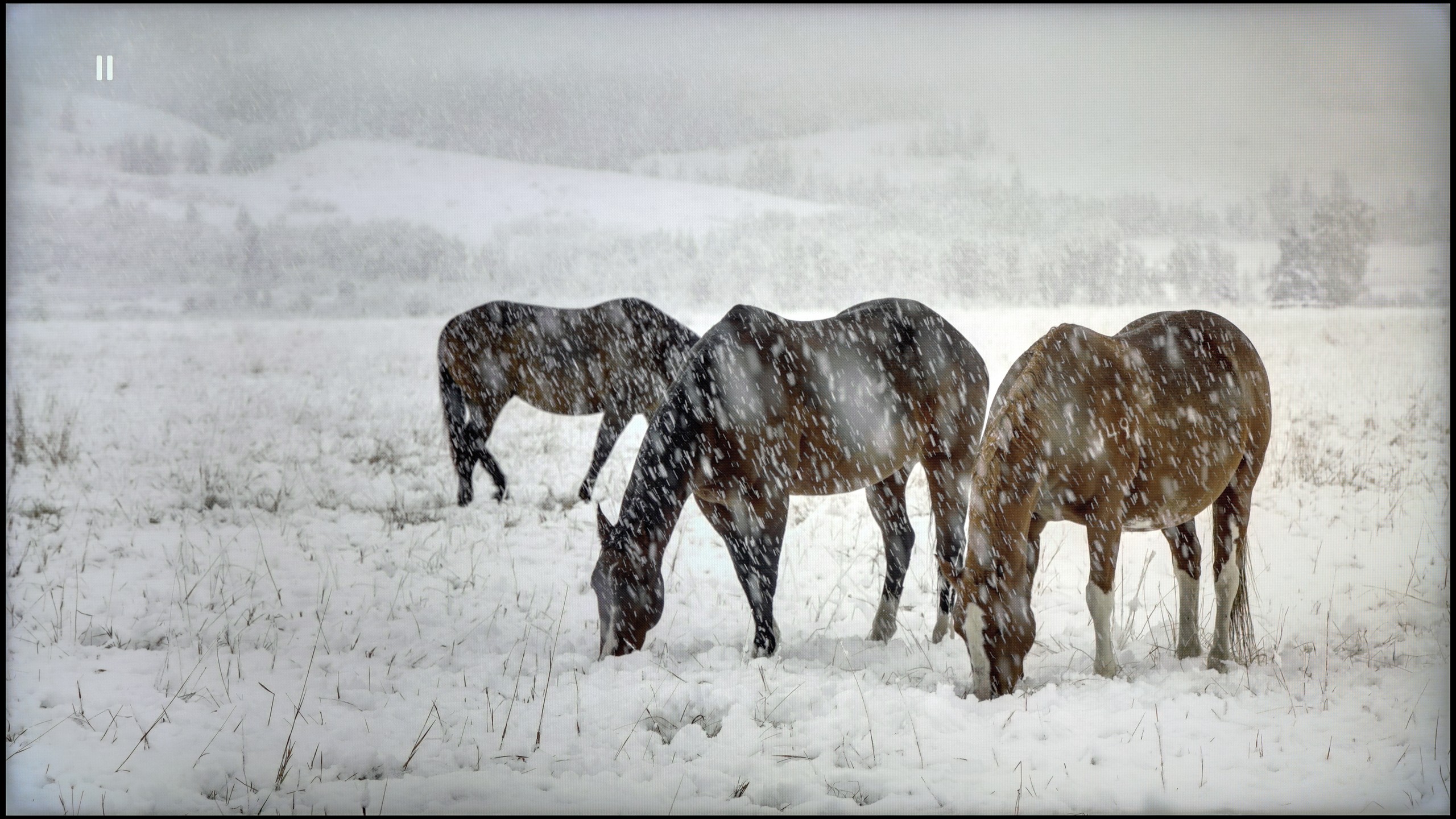
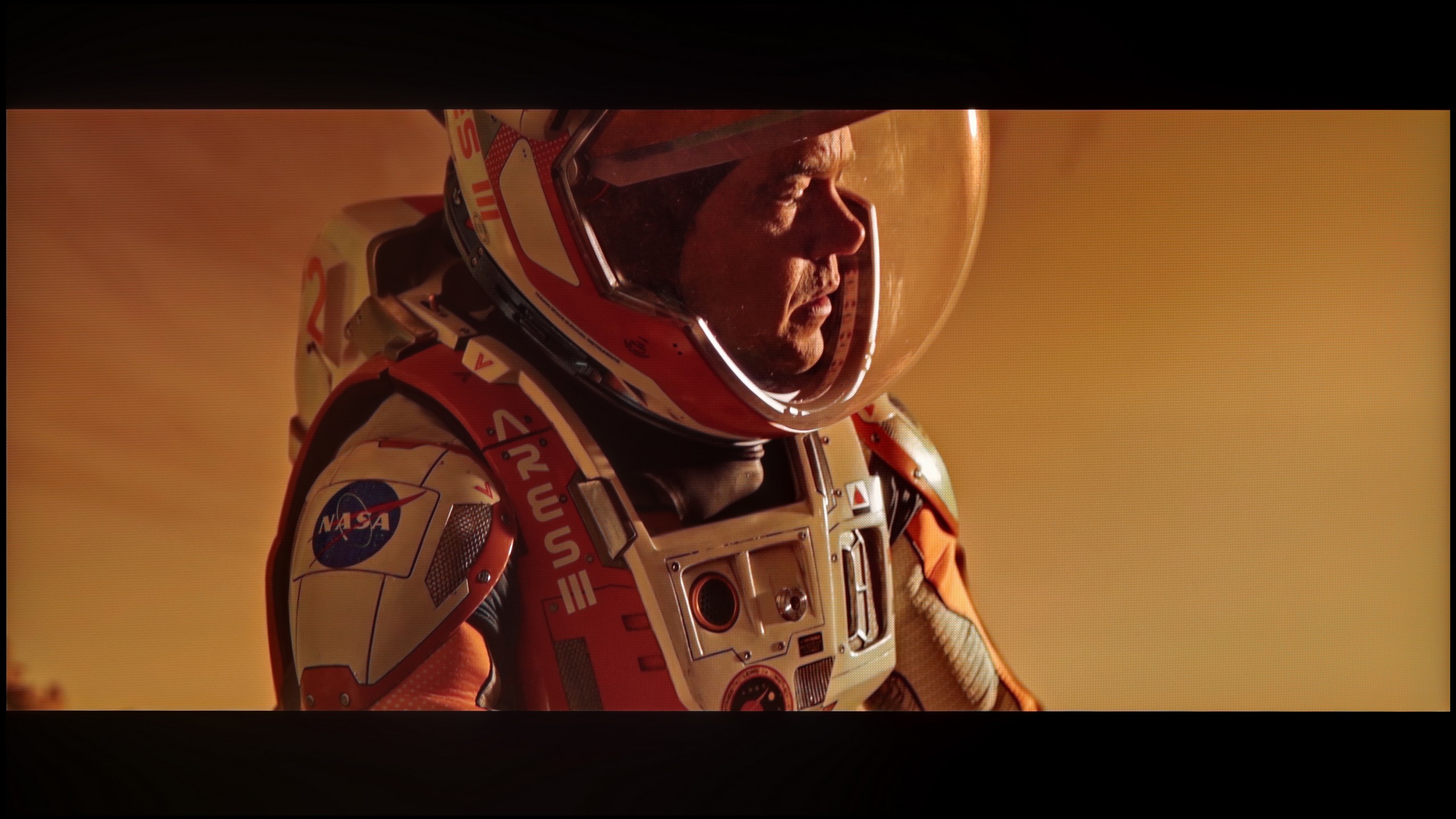
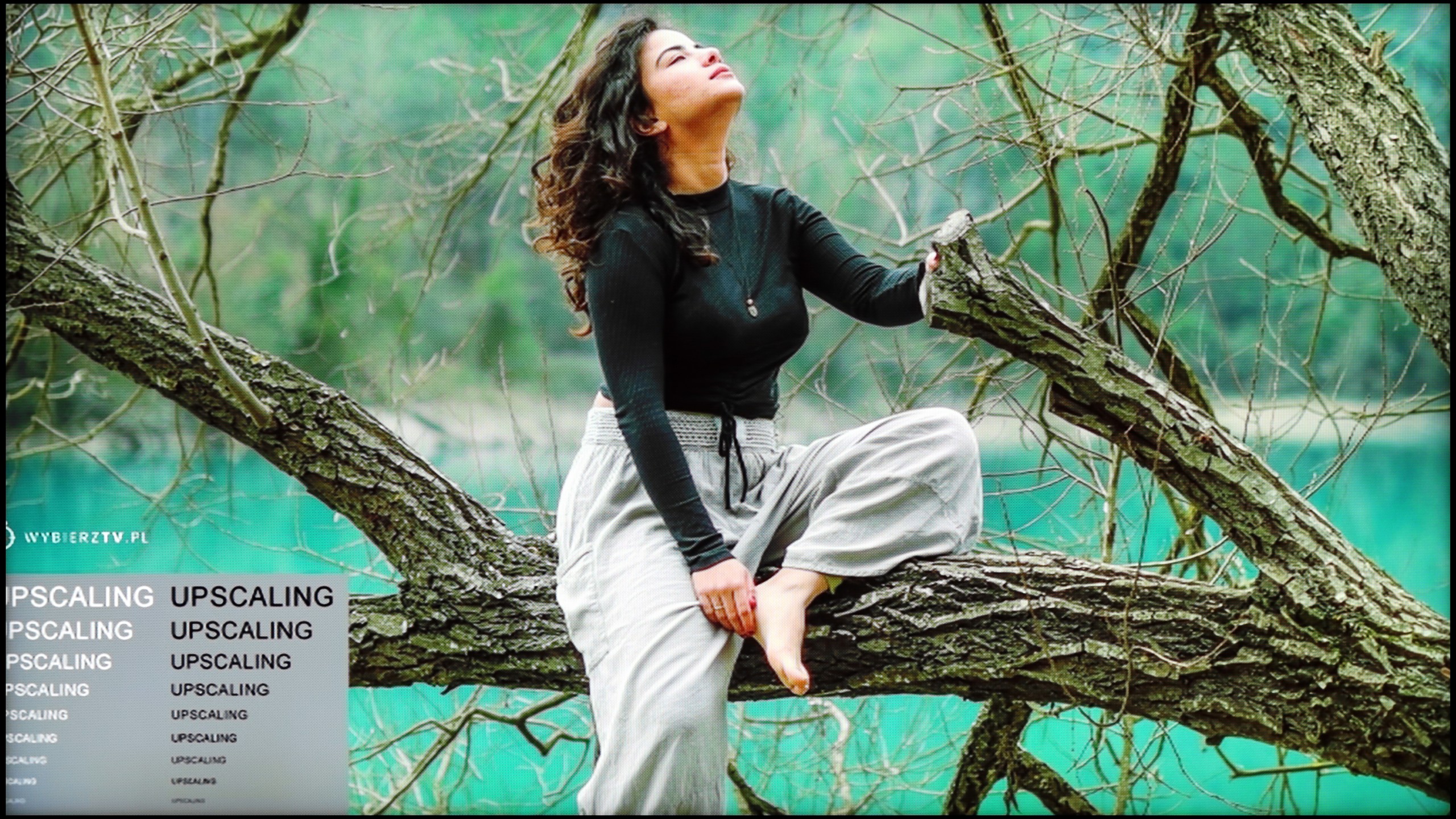
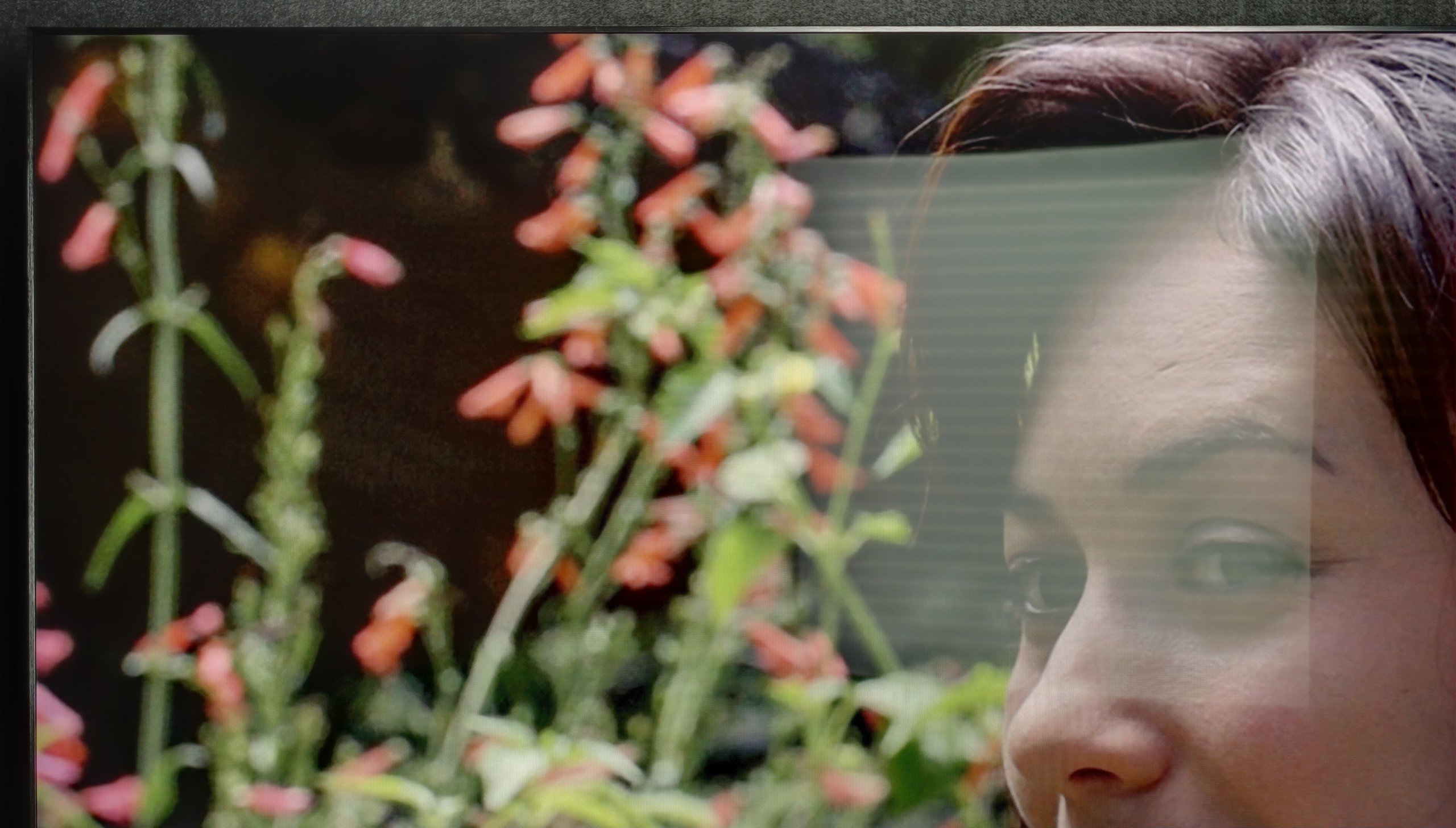
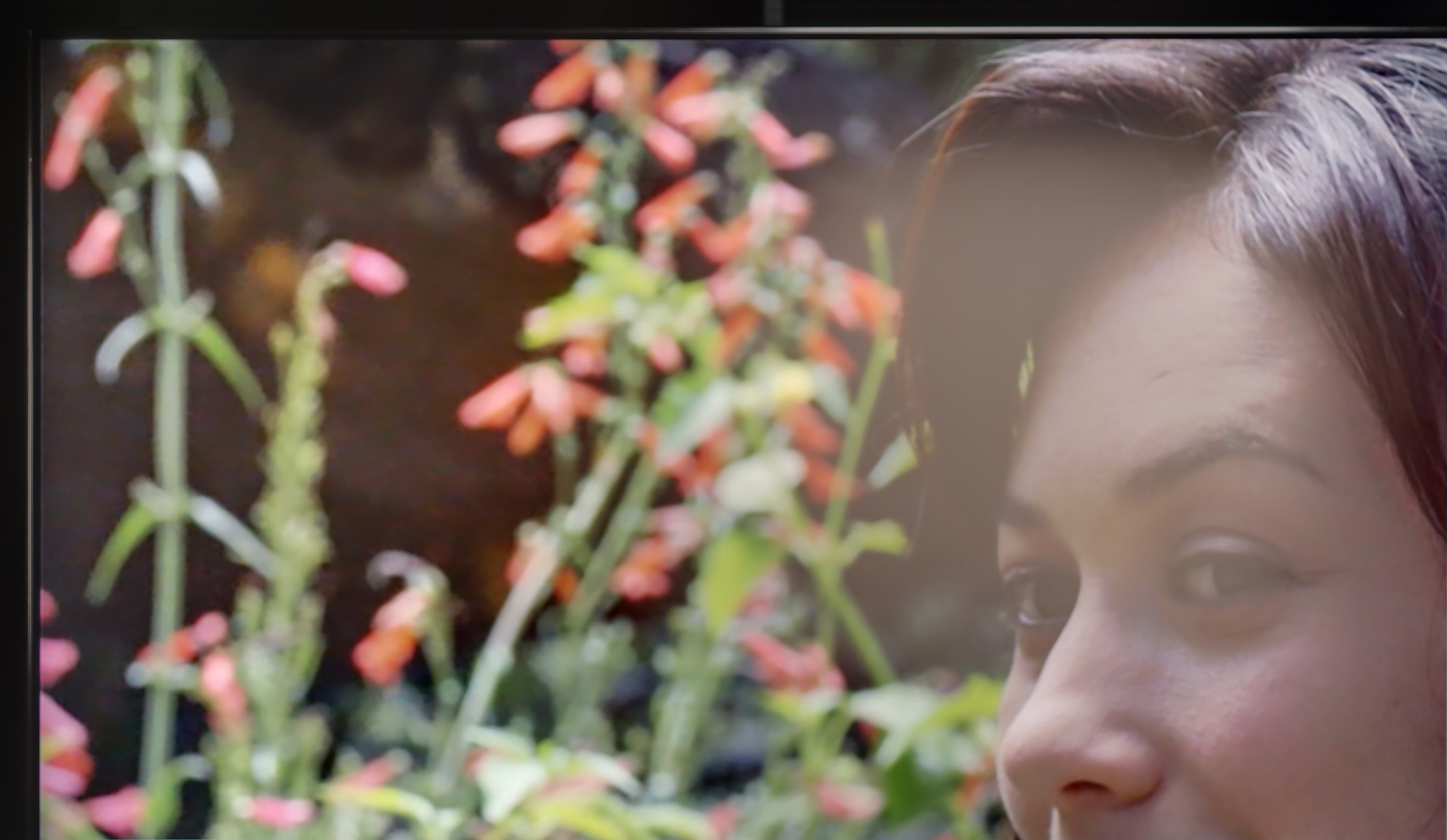
TCL C8K is a really bright television. In synthetic conditions – that is, during tests with brightness charts – it was able to achieve even 3500 nits peak brightness in movie mode. That's an impressive result and brings the C8K close to the market leaders, at least when it comes to panel brightness. More importantly – these aren't just numbers on paper. In films with a lot of bright scenes, such as Life of Pi or The Meg, the brightness clearly exceeds 1000 nits, providing a true sense of HDR effect. The picture in those moments looks very dynamic, colors are saturated thanks to excellent coverage of the color palette, and the lights are – spot on and intense. Exactly how it should be.
However, this doesn’t mean that everything is perfect. Just like in contrast tests, here too, in more demanding scenes, compromises appear. In sequences with very fine light elements – such as stars in the night sky or reflections in dark rooms – the local dimming algorithm can… get confused. Instead of bringing those details up, the television sometimes decides to dim them significantly – down to around 300 nits – to maintain deep blacks. On one hand, this is quite a sensible approach (better deep black than a grey/navy blue screen), but on the other – there may be moments when certain elements of the picture become difficult to see or even disappear into darkness.
TEST UPDATE (20/08/2025): The brightness control algorithm in this model is quite problematic – attempting to calibrate the picture so that it doesn’t drastically overexpose the brightest scenes results in unnatural shifts: improvement in one part of the image results in deterioration in another. The television may achieve slightly higher readings in brightness measurements, but in practice, this comes with a heavily overexposed image that looks very unnatural!
For the record, we provide brightness values without this adjustment:
1463 nits
640 nits
1368 nits
468 nits
1025 nits
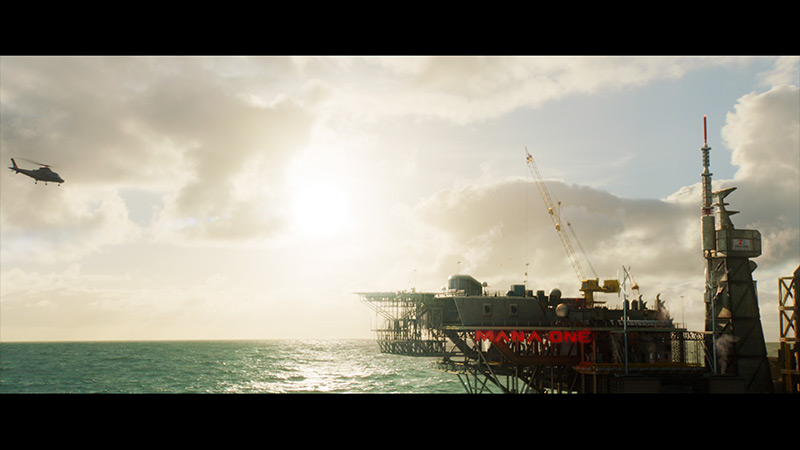
Samsung QN90F can really shine with brightness. In our measurements, it reached even over 2200 nits, which directly translates to the viewing experience. In practice, this means that when a very bright scene appears in a film – for example, a sunrise in The Meg – the screen looks as if natural light is actually shining on us. This isn't just a number from a table, but a real sense of image intensity! However, the TV can't always deliver its full power. With smaller details, such as spotlights or lamps, brightness drops to 500–700 nits. This is a deliberate decision by the algorithms – by doing this, the contrast between large and small elements is better controlled, and the image doesn't lose balance. Importantly, this is still a huge improvement compared to last year's QN90D, where similar details were almost invisible, shining at just 200 nits. Here, the HDR effect is much more cohesive and credible. The only downside is the colours. The coverage of the DCI-P3 spectrum has plateaued at 91%, which can be considered a rather average result in this price range.