Philips MLED920 is a natural continuation of last year’s PML9000 model, but it’s not a rehash. It’s clear that the manufacturer has done their homework – primarily, the local dimming algorithms have been improved, which last year could really spoil the viewing experience. Now, black levels and contrast are definitely better, and combined with Dolby Vision here, even HDR content looks quite decent. The picture can sometimes shine where it should, and it doesn’t strain the eyes in more challenging scenes. Undoubtedly, the greatest asset of the MLED920 is its unique Ambilight system. The three-sided backlighting can give films and games a whole new atmosphere – it’s as if the screen is extending beyond its boundaries, and the whole room becomes part of the viewing experience. This is something that will be appreciated not only by movie buffs but also by gamers, who, in addition to the lights, get a full set of features typical of modern gaming TVs: 144 Hz, VRR, ALLM, and Dolby Vision Gaming. In this regard, Philips has a lot to offer. But. Well, there’s a big but – this is where we reach the most difficult part of this verdict – it’s still a dual-purpose device. On one hand, we have strong picture quality and the unique Ambilight feature, on the other, there are hardware limitations that are hard to ignore. Titan OS in its current form is a big hindrance, full of bugs and shortcomings that make the TV lag behind the competition. Added to this is the price, which is by no means low for the features offered. Therefore, it’s hard to recommend it unequivocally to everyone. However, if you’re looking for Philips' brightest screen at a reasonable price, with Ambilight, a full set of features for gamers, and basic apps – the MLED920 will be quite a good choice.
- Matching (Score)
- Our verdict
- TV appearance
- Where to buy
- Contrast and black detail
- HDR effect quality
- Factory color reproduction
- Color reproduction after calibration
- Smoothness of tonal transitions
- Image scaling and smoothness of tonal transitions
- Blur and motion smoothness
- Console compatibility and gaming features
- Input lag
- Compatibility with PC
- Viewing angles
- Daytime performance
- Panel details
- TV features
- Apps
- Playing files from USB
- Sound
Philips MLED920 / MLED910 vs Haier Q80FUX
Direct comparison
MLED920 / MLED910


Panel type: LCD VA
Resolution: 3840x2160
System: Titan OS
Model year: 2025
Complete the survey to find out the result

Panel type: LCD VA
Resolution: 3840x2160
System: Google TV
Model year: 2025
Complete the survey to find out the result

Overall rating
6.5
5.8
Movies and series in UHD quality
6.4
5.9
Classic TV, YouTube
6.8
5.6
Sports broadcasts (TV and apps)
6.8
4.7
Gaming on console
8.5
6.7
TV as a computer monitor
4.0
6.0
Watching in bright light
5.5
4.8
Utility functions
5.5
5.6
Apps
6.7
9.6
Sound quality
6.2
5.5
Complete the survey to find out what fits your preferences
Advantages
Solid black and high contrast thanks to mini-LED backlighting
HDR brightness reaching 700–800 nits in real movie scenes
Support for multiple HDR formats including Dolby Vision and HDR10+
Ambilight – an element that adds atmosphere, especially in the evening
A lot of supported audio formats: DTS:X, Dolby Atmos, Dolby True HD 7.1
144 Hz panel with support for VRR, ALLM, and Dolby Vision Gaming
Loud sound (up to 88 dB)
Illuminated remote
Very good native contrast and decent black (thanks to the VA panel)
PFS / QLED Filter - Wide colour gamut (about 95% DCI-P3)
Remarkably low input lag (below 10 ms at 120Hz and about 12 ms at 60Hz), making it a great choice for fast-paced games.
Support for 120Hz at lower resolution (Full HD) and the presence of VRR and ALLM
Support for Dolby Vision
Well-functioning file player via USB
Presence of analogue headphone output (jack)
Disadvantages
Titan OS is quite underdeveloped – there are significant errors and missing features in the applications
Few user-friendly features
Hybrid infrared remote
Issues with the smoothness of tonal transitions in dark scenes
The television is not suitable (aside from gaming) for working with a PC – strong dithering and poor readability of fonts, especially coloured ones and on dark backgrounds
The image is quite "blown out" in HDR
Google TV software is full of bugs, poor translations, and issues
Lacks any image enhancement features (noise reduction, gradient smoothing)
Average brightness
Flat, bass-less sound
High input lag in Dolby Vision mode for gaming
Weird and not very ergonomic remote
Our verdict
The Haier Q80FUX television is one of the most schizophrenic propositions we have had in our editorial office for a long time. On one hand, we have a solid piece of equipment: a VA panel guaranteeing deep blacks, as expected for this segment, and a QLED quantum filter that can indeed generate juicy, eye-catching colours. This is the foundation on which a truly competitive mid-range receiver could have been built. Unfortunately, all this potential of the matrix is systematically undermined by the software, which is a real anchor for this model. The biggest Achilles' heel of the Q80FUX is its total capitulation in dealing with HDR10 materials. The electronics seem to completely misunderstand how to interpret the signal, resulting in it consistently blowing out the brightest parts of the image, turning them into a flat, milky spot. Adding to this is the Google TV system, which – while functional – is unstable, full of bugs and annoying oversights, giving us an image of a raw product that clearly reveals the producer's lack of experience. Just when we were about to write this model off, we discovered its surprising niche. After connecting a console, the Q80FUX undergoes a transformation. It turns out that this television offers remarkably low input lag, fully supports VRR, and can handle a 120Hz signal in Full HD resolution. In the gaming world, where responsiveness is everything, these parameters put it in a very good light. So we are dealing with a device of very narrow specialization. It is not a universal living room television – it lacks stability and, above all, any correctness in handling films. It is rather a budget, large-format monitor for gamers, who can consciously forgive it all the software flaws in exchange for those few key attributes for console/PC at a relatively affordable price.
TV appearance
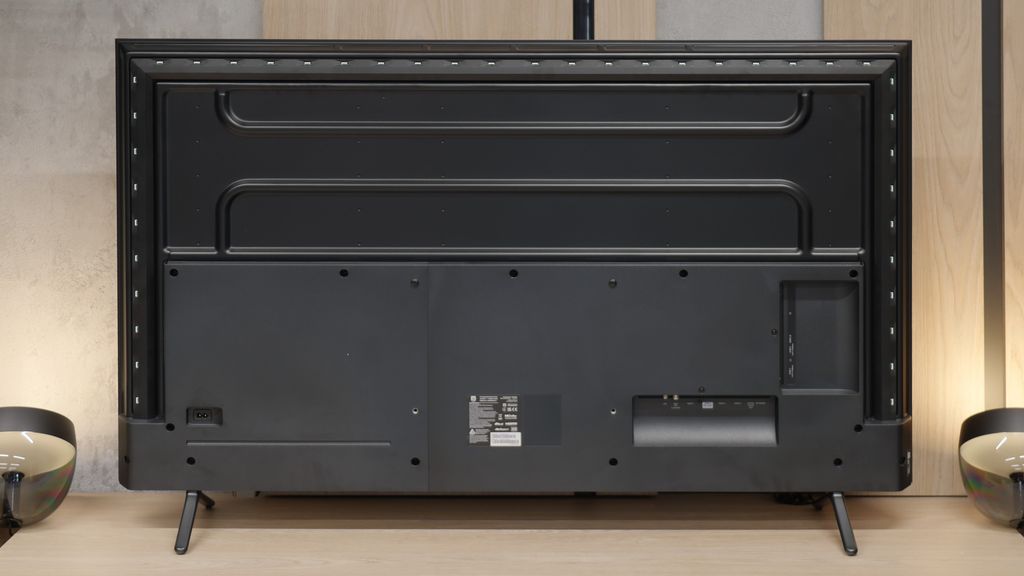
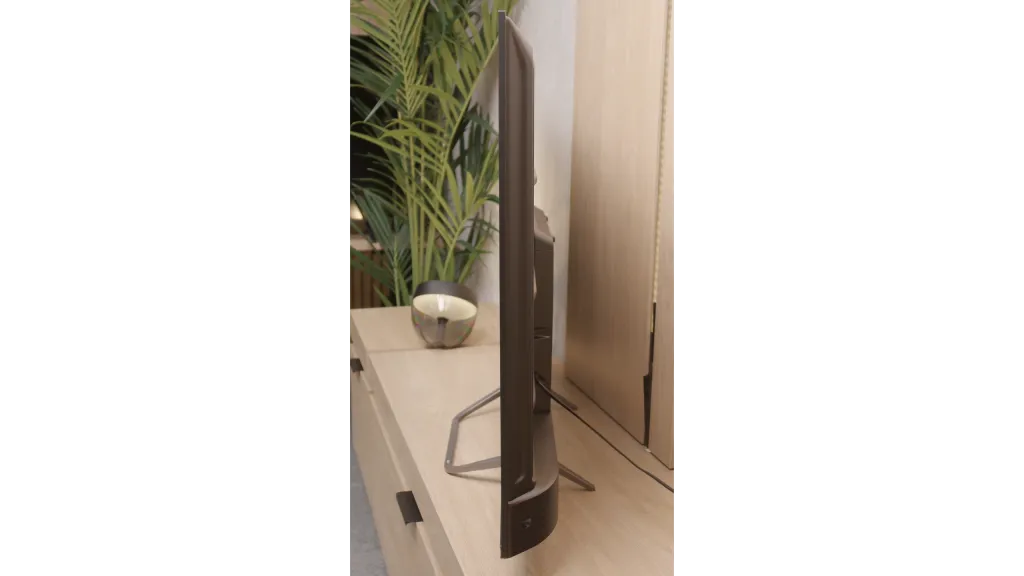
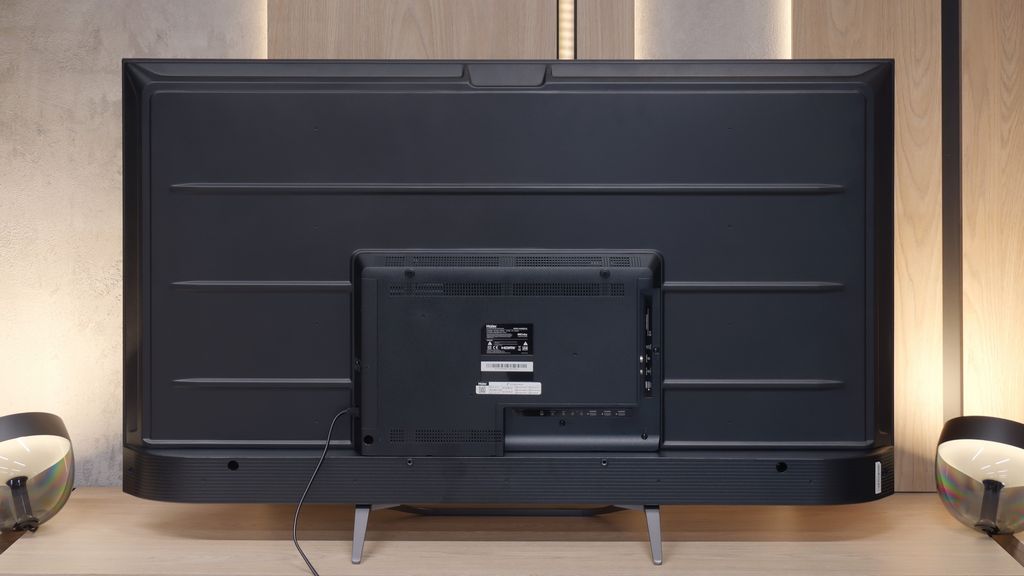








Contrast and black detail
7.9/10
6.3/10
Local dimming function: Yes, number of zones: 144 (12 x 12)
Local dimming function: No
Contrast:

Result
298,900:1

Result
38,500:1
Result
23,950:1

Result
16,850:1

Result
8,000:1

Result
5,200:1

Result
7,400:1

Result
7,550:1

Result
7,300:1

Result
6,450:1
Halo effect and black detail visibility:


Philips MLED920 in the 55-inch version that we had the opportunity to test uses a high-contrast VA panel. The panel itself is one thing, but the real standout feature of this model is the mini-LED backlighting. This largely determines how black and contrast look – and it must be said that Philips has taken a big step forward compared to the models from 2024, where the local dimming algorithms performed just average. In this new version, it is significantly better, and the contrast presented by the MLED920 can truly surprise in a positive way. At times, it even approaches the level known from the best LCD TVs on the market – blacks can be deep, the image gains a three-dimensional quality, and viewing experiences in a dark room leave a great impression. Of course, as with any mini-LED TV, this is not an image completely free of compromises. With a large number of small elements on the screen, the local dimming algorithms can sometimes get confused – at times dimming details more than we would like and other times brightening the background, resulting in slight, light blue halos around objects (the so-called halo effect). Despite these imperfections, we must emphasize that black and contrast are truly strengths of the Philips MLED920 and definitely one of the reasons to consider it in the mid-range segment.
I must admit that approaching a TV in this price range, one instinctively crosses their fingers, hoping that at least the black won't be a grey blotch. Meanwhile, the Haier Q80FUX, specifically the 55-inch unit we have in our office, can pleasantly surprise in this regard. Its secret lies in the use of a VA panel, which tends to generate high contrast by nature. And these are not empty promises. During screenings, in the majority of film scenes, the contrast reported itself at levels ranging from 5000:1 with commendable regularity, often reaching as high as 8000:1. These are really strong results, considering the fact that this TV has no, not even minimal, form of local dimming. Translating this into couch-side experiences: for its price point, the Q80FUX offers solid black levels. Of course, it isn’t that perfectly velvety depth that makes the screen disappear into darkness. When we conduct a viewing in total light isolation, we can see that in the darkest parts of the image, the black betrays its budget origins, subtly shifting towards a bluish glow. However, this is a defect that is easy to mask – just a bit of light from a lamp in the corner of the room is enough for this nuance to become invisible, and the image regains a satisfying depth.
HDR effect quality
5/10
4.9/10
Luminance measurements in HDR:

Result
722 nit

Result
177 nit

Result
775 nit

Result
131 nit

Result
677 nit

Result
308 nit

Result
327 nit

Result
352 nit

Result
330 nit

Result
344 nit
Scene from the movie “Pan” (about 2800 nits)


Scene from the movie “Billy Lynn” (about 1100 nits)
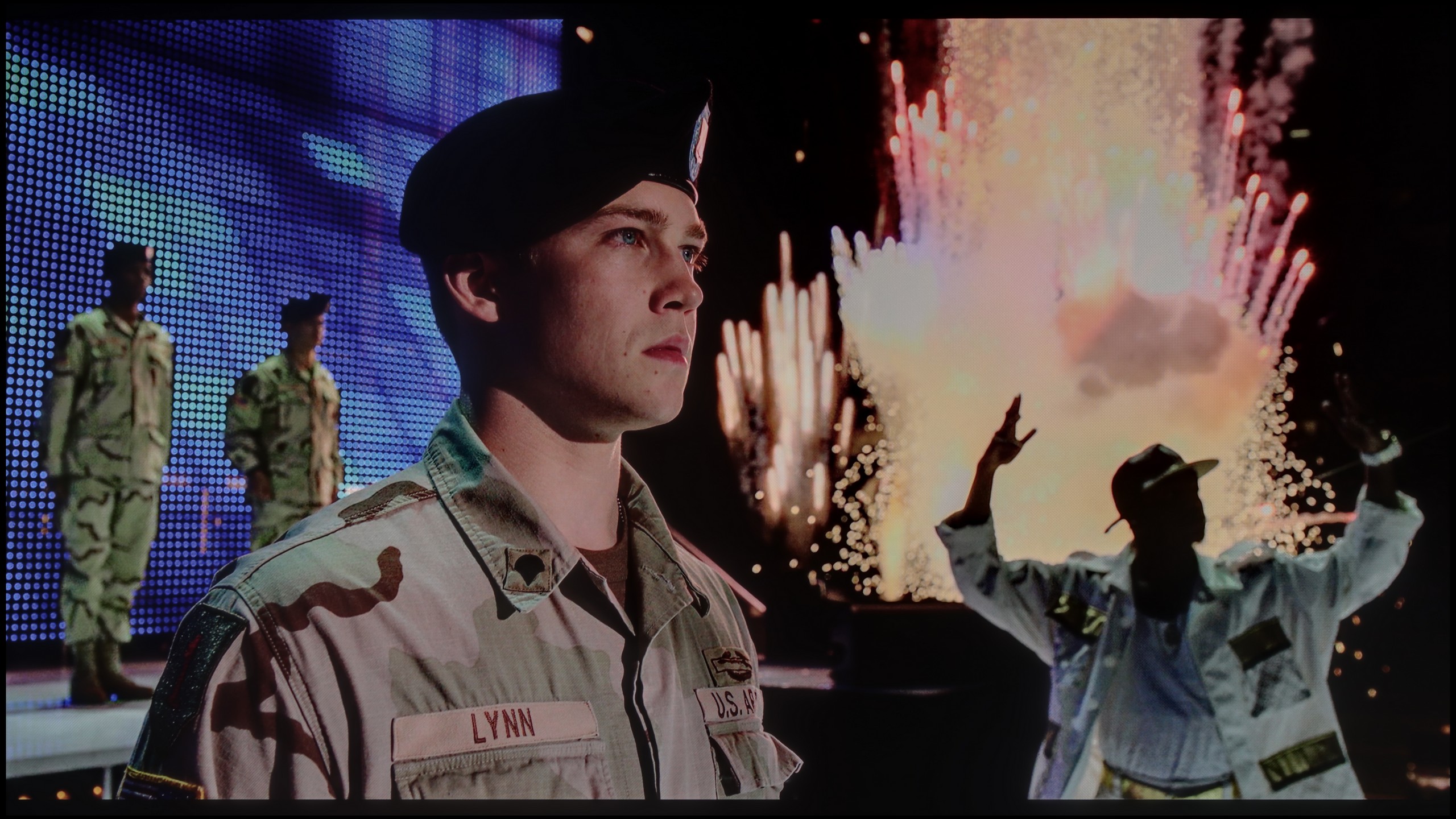


Static HDR10


Dynamic: Dolby Vision
Dynamic: Dolby Vision


HDR luminance chart:
Haier Q80FUX
HDR luminance
Philips MLED920 / MLED910
HDR luminance
Philips MLED920 in our measurements in static tests even reached around 900 nits, which for a mid-range model is quite an impressive result. In practice, this translates to a lot of satisfaction during viewing – in scenes rich in bright light, such as the first, third, or fifth test patterns, the screen was able to generate around 700 nits, which is sufficient to feel the real "HDR effect". However, it cannot be denied that the limited number of backlight zones and the typical mini-LED compromises in dimming algorithms reveal their flaws in more demanding scenes. In sequences with small light sources – like the moon or a scene from the film Sicario 2 – the television clearly prioritises maintaining deeper blacks at the expense of the brightness of these small elements. For most viewers, this is still a reasonable compromise, as the dark background looks much better, although it should be noted that the details themselves may not dazzle with intensity. The question of colours also leaves a bit to be desired. Although the employed PFS filter (the equivalent of quantum dots known from QLEDs) does its job and the colours appear quite vibrant, the coverage of the DCI-P3 colour space reaches "only" 90%. In everyday viewing, this will be sufficient, but in extremely colourful productions – like the latest Disney animations – one can notice that some tones are not as vivid as they could be in other constructions.
Alright, let's move on to the topic that really sparks discussions, which is the capabilities of the TV in HDR mode. Let's be clear from the start: the Haier Q80FUX is certainly not a brightness demon. The panel of this set can generate about 350 nits at peak, which in today's reality is an absolute minimum to even talk about the presence of HDR expanded dynamic range. On the plus side, this brightness is at least stable – regardless of the test pattern or film scene we used, measurements consistently hovered around 300-350 nits. These are at best adequate results, definitely far from the dazzling display of capabilities that we know from more expensive models. Fortunately, there is one aspect where the Q80FUX makes up for these shortcomings and does so considerably. We are talking about a QLED TV (or more precisely PFS LED), which means that thanks to the quantum dot filter used on the panel, it can generate truly juicy, vibrant colours. These are not empty promises – covering nearly 95% of the DCI-P3 colour gamut is an impressive result and directly translates into very pleasant, saturated colours for the eye.
Factory color reproduction
5/10
4/10


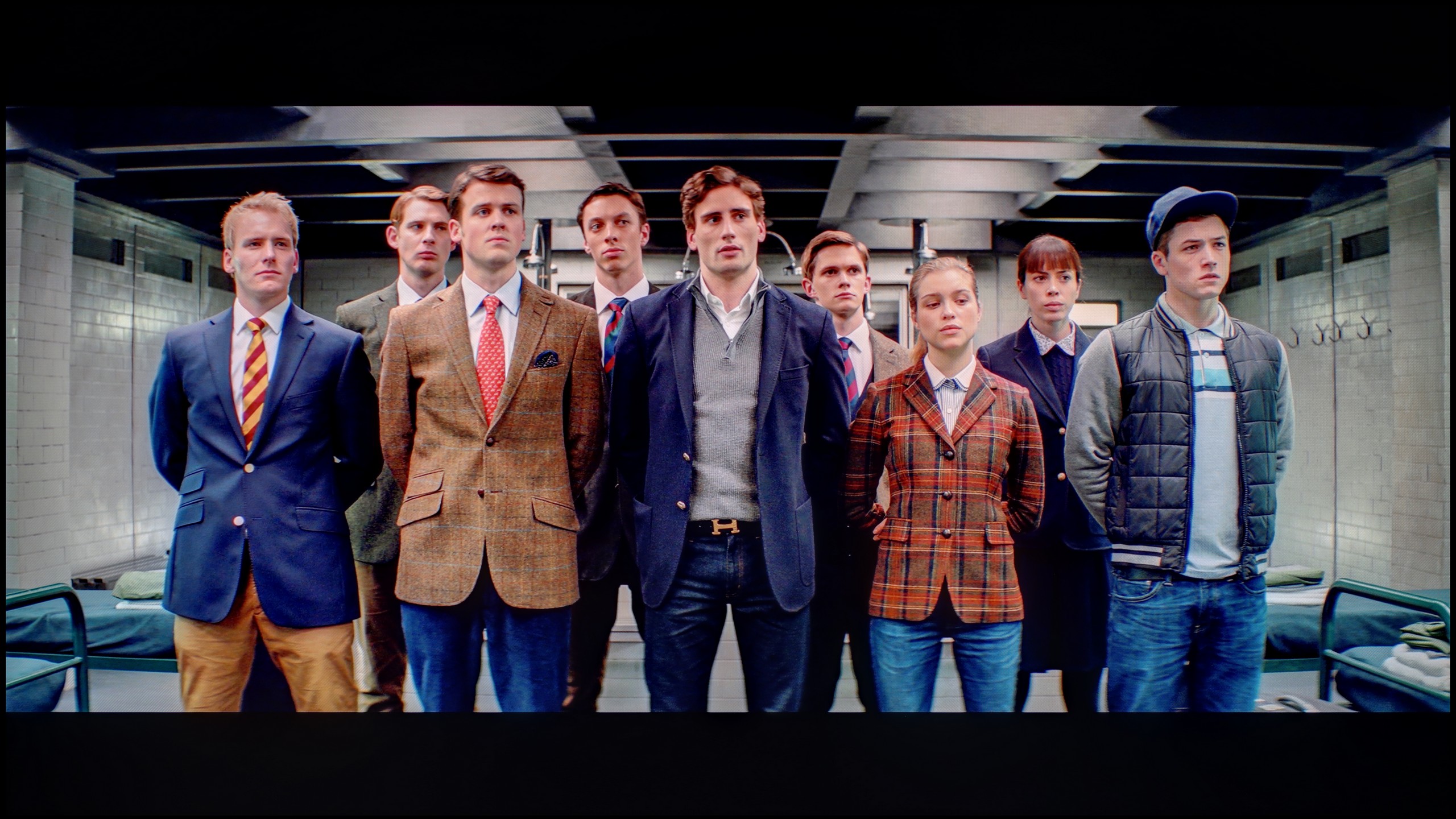
Factory Mode
After calibration
Like every Philips TV we've tested, the MLED920 was primarily assessed in Filmmaker mode – the so-called "most honest" mode, designed for films and to faithfully convey the intentions of the creators. Indeed, in terms of colour accuracy, it performs best among all the modes available on the TV, but it is not without flaws. The first thing that stands out is the white balance. The image has a slight tendency towards purple-pink tones, giving it a somewhat unnatural character. However, an even bigger problem turned out to be what we mentioned earlier – image clipping. Just looking at the gamma or EOTF charts reveals that the line deviates significantly from the norm, dropping below a value of 1.8. In practice, this means "bleeding" of the brightest whites, where the image becomes almost milky. Fortunately, most of these issues can be corrected – the MLED920 responds to calibration, and with a few adjustments, image quality can be significantly improved.
Factory settings for movie mode are seldom perfect, but in the case of the Q80FUX, we encountered a noticeable imbalance. In SDR content, the image was definitely too warm, due to an excessive amount of red in the white balance, giving the overall picture a slight sepia tone. Conversely, in HDR materials, the television fell into the other extreme – an excess of blue caused an unnatural, cool effect in perception. However, it wasn't the fickle white balance that was the biggest issue with this TV. The real culprit, responsible for the previously described problems, was hiding deeper. It turned out that the Q80FUX has completely miscalibrated gamma values and, crucial for HDR, a poorly executed EOTF curve. It was these erroneous factory settings that caused the notorious clipping of the brightest parts of the image, imposing that characteristic milky filter over them. Thus, we found the source of the problem. This situation led to general, significant colour inaccuracies that were easy to catch even for an untrained eye. Like every television we tested, we decided to calibrate this model as well, and you can find the results of these adjustments in the next paragraph.
Color reproduction after calibration
7.5/10
6.1/10
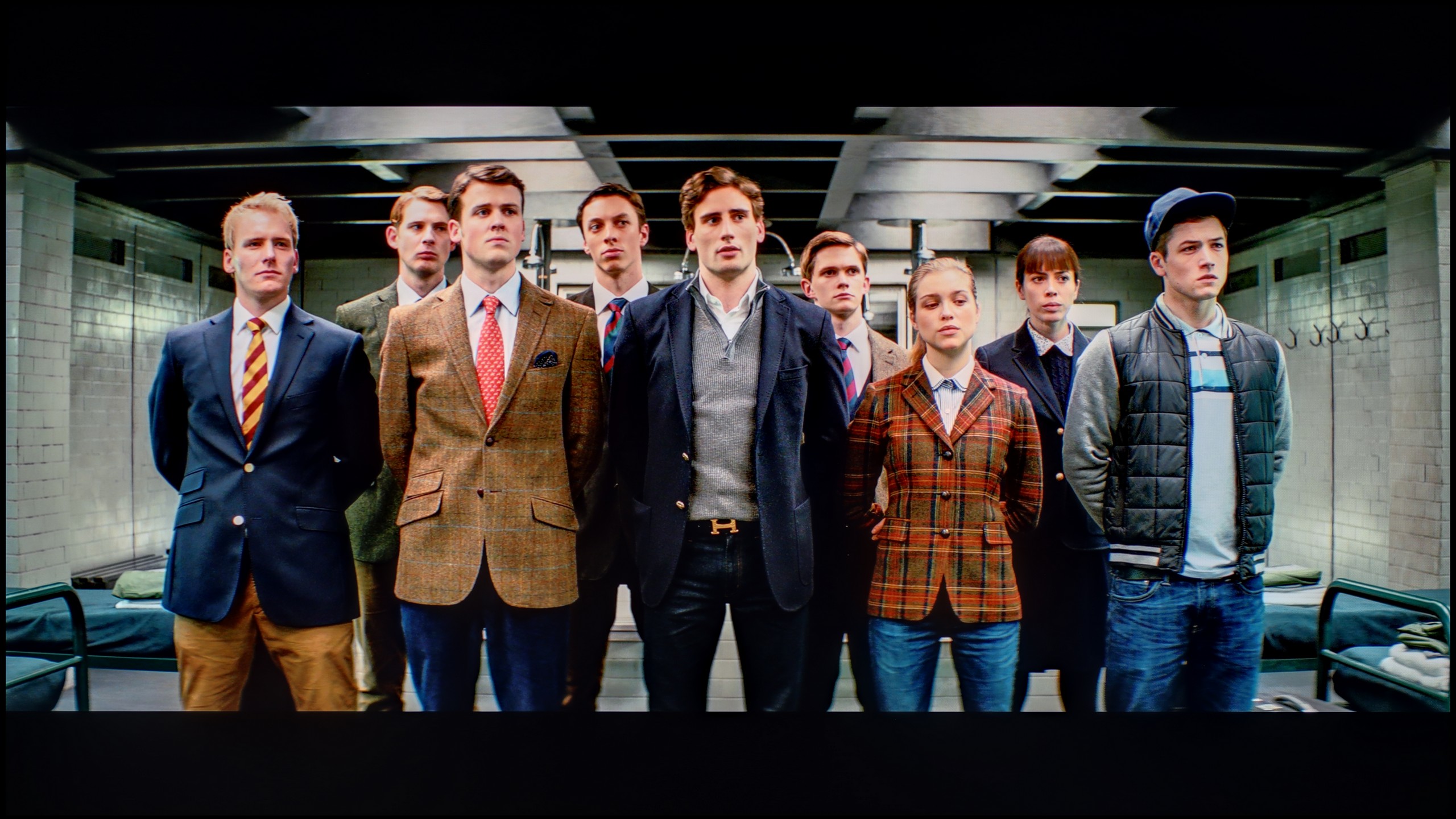




After calibration, we managed to largely tame the white balance – to the extent that the average viewer will not be able to detect colour inaccuracies. The characteristic pink-purple glow that previously disrupted the naturalness of the image has also disappeared. The colour palette has been organised, and the colours appear more cohesive and neutral. The gamma in SDR content looks really good after calibration – there’s no sign of the earlier “bleeding” effect in bright scenes. The image has become more contrasty and free from the milky effect that previously severely affected the viewing experience. In the case of HDR content, the improvement is also noticeable, although here it is still evident that the television goes “its own way”. The EOTF curve cannot be fully adjusted, as Philips simply does not offer tools for precise control of this parameter in its settings. In many films, the television still exposes the image “in its own way”. Despite these limitations, calibration has brought a lot of good – the majority of colour inaccuracies have been minimised and the overall image balance has significantly improved. However, one must remember that certain barriers arise from the very hardware construction and simply cannot be overcome.
The results of our calibration procedures must, unfortunately, be regarded as twofold. Generally speaking, the picture is undeniably better than before the adjustments; however, the biggest winner of this process has been SDR content. It is precisely here, after correcting the gamma curves and white balance, that we achieved results that can safely be called very good. Once set up, the Q80FUX truly shines in standard dynamic range, displaying only slight errors in the most challenging skin tones. Unfortunately, the weakest link remains HDR content. And here's the paradox: even though we managed to calibrate the white balance to near perfection, the overall colour errors still remain at quite a high level. The reason is that the television still interprets the static HDR10 metadata "in its own way," stubbornly enforcing that unfortunate image clipping effect, which inevitably leads to significant distortions. Although we successfully eliminated the factory excess of blue, due to this electronic interference, the screen can still veer into somewhat too cool tones. That’s just how this television is.
Smoothness of tonal transitions
6.5/10
7.5/10












The fluidity of tonal transitions in the Philips MLED920 is not its strongest suit. In our tests, we quickly noticed that the television has noticeable issues in darker scenes – examples include segments from the film The Green Knight or test grey palettes. There, you can see characteristic banding of colours and too harsh transitions between shades, which can be quite noticeable in productions with a darker aesthetic. Fortunately, the situation looks better in brighter scenes – there, the image presents smoothly and without significant artifacts.
Analysing the ability of the television to handle subtle tonal transitions, or "banding", leads us to some interesting conclusions. The Haier Q80FUX seamlessly blends adjacent colours in most scenes, creating a smooth, cohesive image. However, this process is not without its flaws. During our tests, we noticed minor issues and imperfections in each of the test scenes we used. These may not be errors that aggressively jump out and ruin the viewing experience, yet their presence is worth noting. Interestingly, this receiver does not exhibit any particular weaknesses or strengths in this regard – it handles this challenge in exactly the same way, regardless of whether it is displaying delicate gradients of a bright sky or dark transitions in shadows.
Image scaling and smoothness of tonal transitions
7/10
4/10
Smooth transition function

Image without overscan on the SD signal


The manufacturer has equipped this model with several features that improve signal quality, and although we usually approach such “enhancers” with caution, here they prove to be really helpful. The key option is called “distortion reduction” – it works best at a medium level because, on one hand, it effectively smooths out unwanted steps and colour transitions, and on the other, it doesn’t excessively cut details, meaning the image still looks natural.
It’s a bit worse when it comes to upscaling. Lower quality materials – such as the test video with the model – appeared soft and lacking sharpness. Of course, it can be partially adjusted with the sharpness slider in the menu, but the result still falls short compared to what competitors offer at a similar price. Philips still needs to work on this aspect because, in light of the successful improvement of tonal transitions, the upscaling simply comes off weak.
If there's one area where Haier clearly shows it still has a lot to catch up on compared to the market leaders, it's digital image processing. The upscaling, well... it's just okay. And that's really all that can be said about it. It does what it's supposed to do: ensures that lower resolution signals don't scare you with harsh pixelation on the screen and don't look like a forcibly enlarged postage stamp. However, it's far from the finesse and "intelligent" sharpening that more experienced players in this market have developed over the years. The biggest issue with the Q80FUX software is the almost complete lack of additional "cleaning" and smoothing features for the image. The receiver offers no noise reduction mechanisms or gradient enhancement. This means that with older or highly compressed materials, we simply have to accept that all the imperfections in tonal transitions or colour blending, which we mentioned earlier, will constantly accompany us during viewing.
Blur and motion smoothness
7.7/10
4.5/10

Blur (native resolution, maximum refresh rate):






Blur (4K@144Hz):
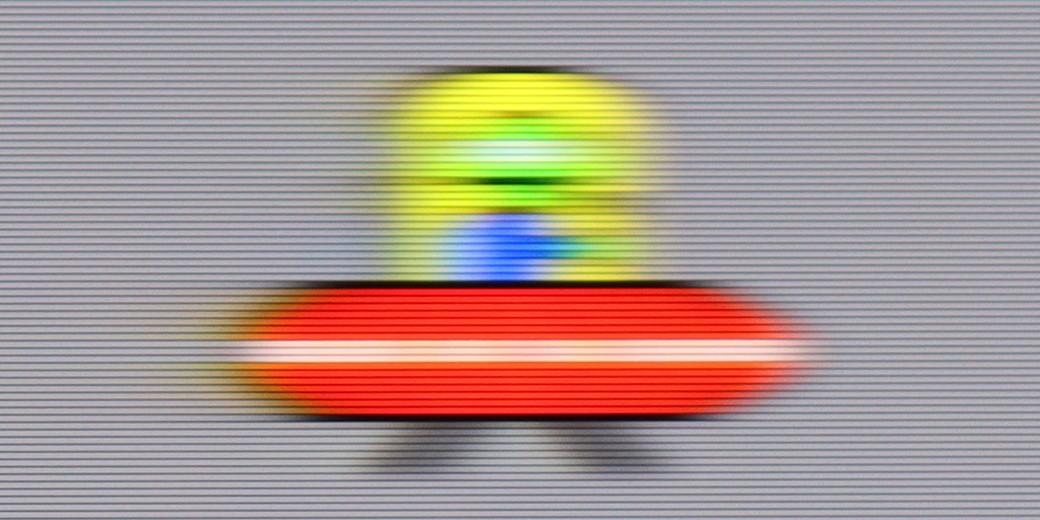
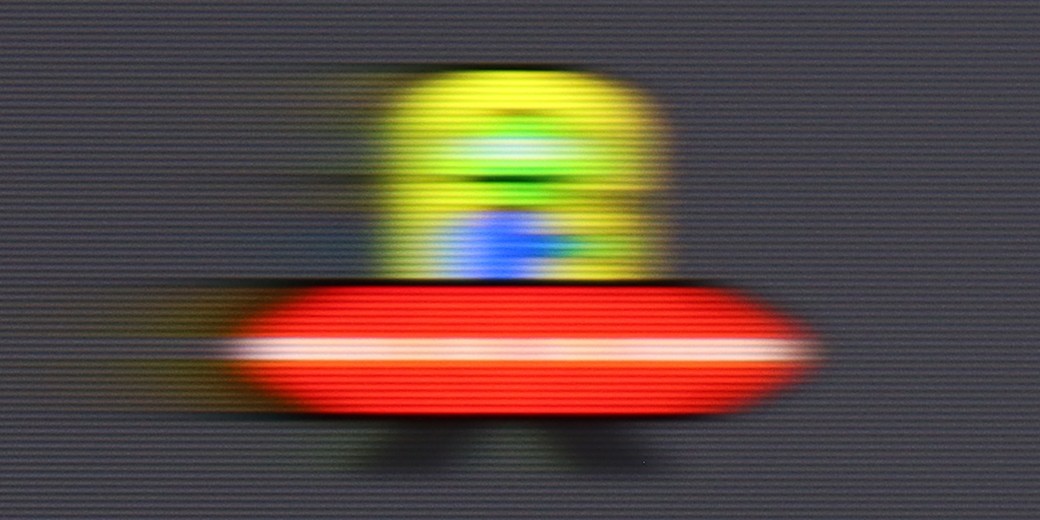



Blur ():
Philips MLED920 features a 144 Hz panel, which immediately suggests that we shouldn’t complain about motion smoothness. And indeed – for a VA panel, the motion blur is relatively low here, and while you can sometimes notice slight issues on darker backgrounds, they’re not something that will catch the eye of most people during regular viewing.
A big plus is also the presence of a motion smoother called “Motion Style.” It allows you to adjust the smoothness to your own preferences – if someone prefers a more “theatrical,” almost television-like character of the image, they can increase the sliders, and if they want to maintain the natural “judders” of a cinematic frame, they just need to set lower values. This way, everyone can find a happy medium.
The issue of motion fluidity and blurring is largely predetermined by the use of a 60Hz panel, which naturally makes it difficult to recommend this receiver to enthusiasts of very dynamic content. Fortunately, in the Q80FUX, we find a few options (although, as will soon become clear, really just one) intended to enhance the experience with older film productions. There is a "De-Judder" slider available, which indeed affects motion fluidity and allows us to adjust it to our preferences: from raw, cinematic frame rates to a more theatrical, smoothed presentation. However, a true surprise awaits us right next to it in the menu. There is also a second slider, supposedly dedicated to removing blur – this is a feature we typically encounter in 120Hz panels, aimed at combating blurring in sports. As we expected, recalling memories from testing the K85F model, here too this slider is merely a façade. Its adjustment contributes absolutely nothing to the picture and simply seems to be an oversight by the product engineers who left a non-functional option in the software for this type of panel.
Console compatibility and gaming features
9.8/10
5.6/10
- ALLM
- VRR
- VRR range48 - 144Hz48 - 120Hz
- Dolby Vision Game Mode
Yes, high input lag
- Correct implementation of HGIG
- 1080p@120Hz
- 1440p@120Hz
- 4K@120Hz
- Game bar
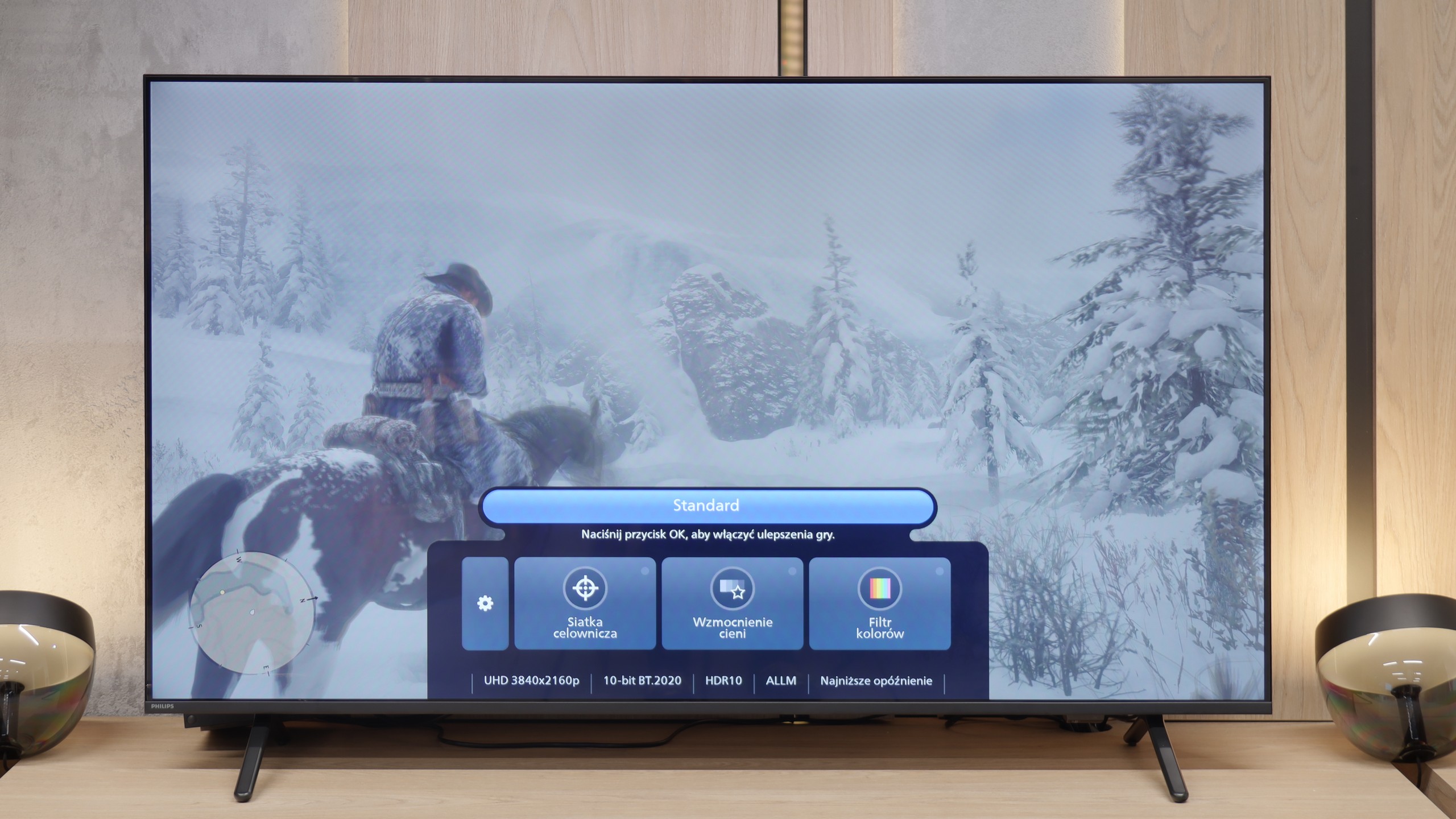
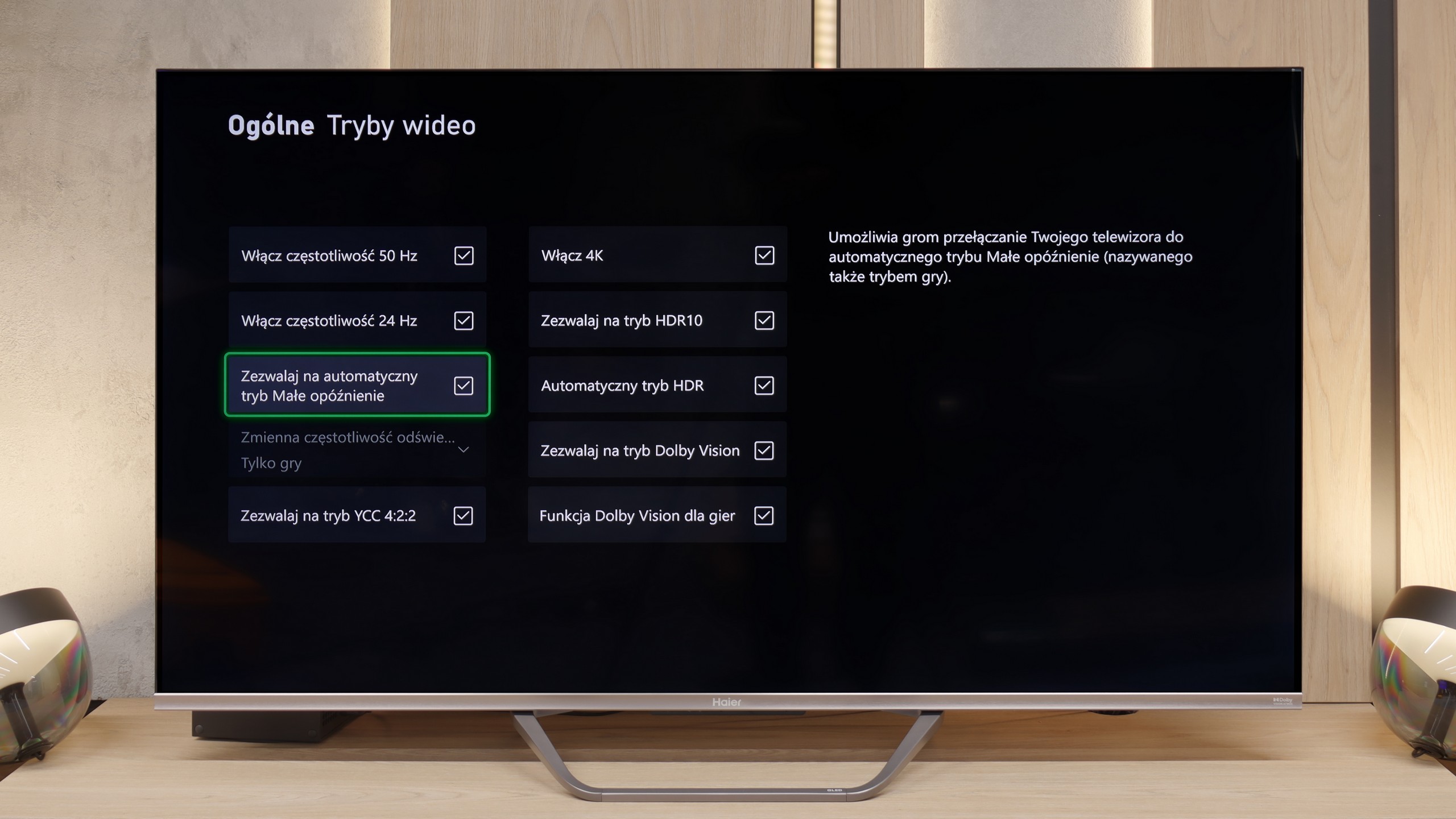
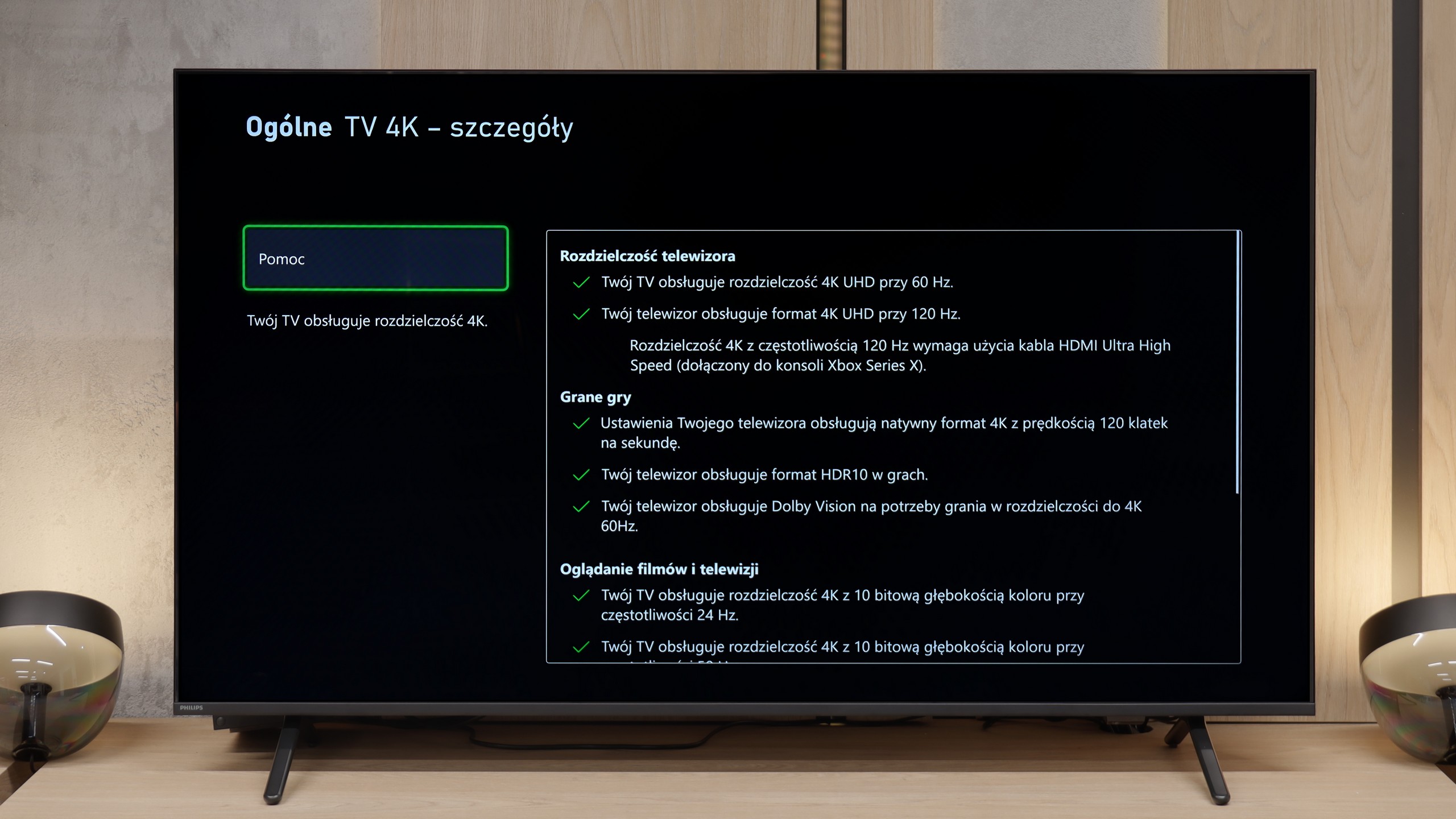
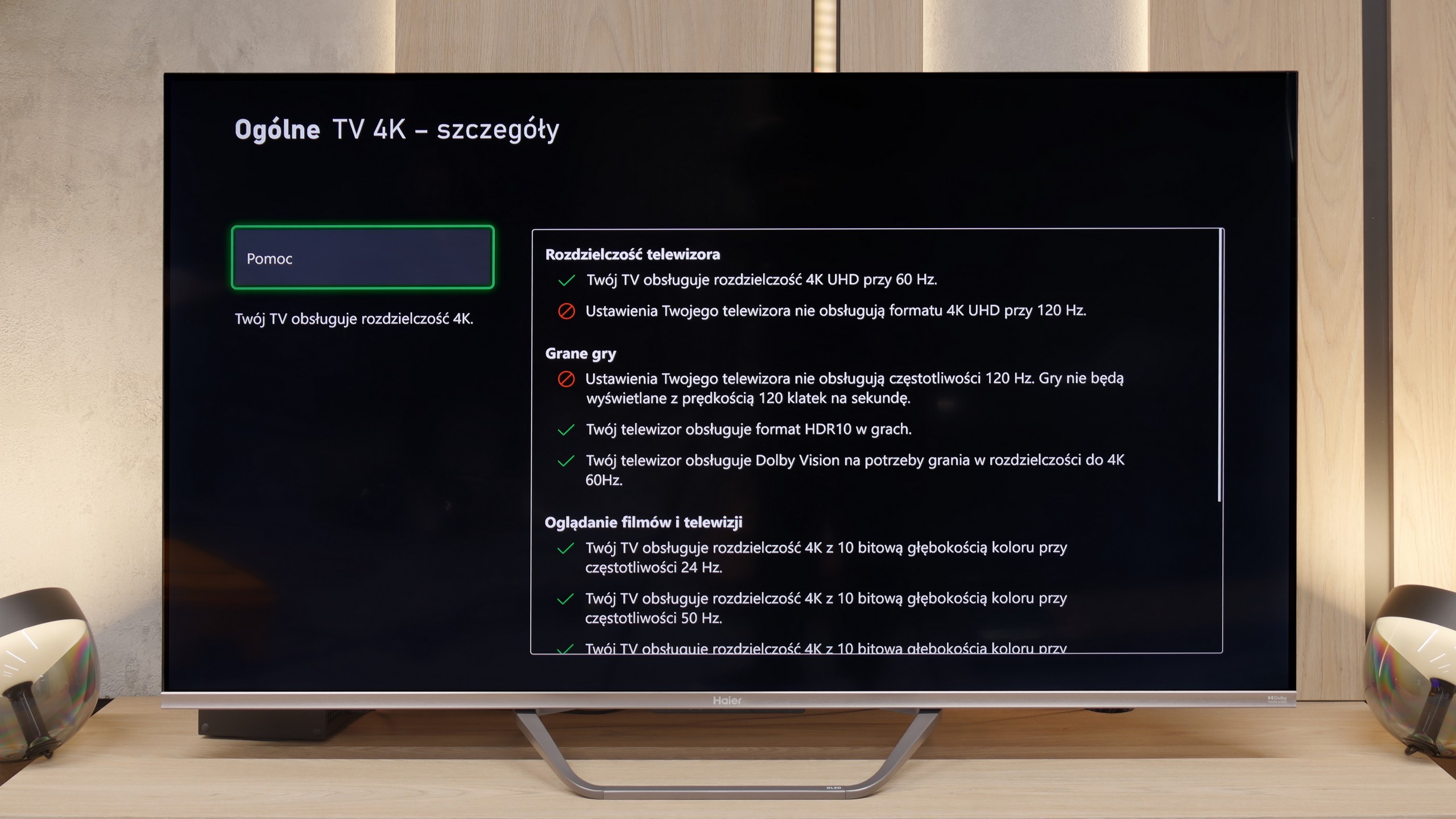

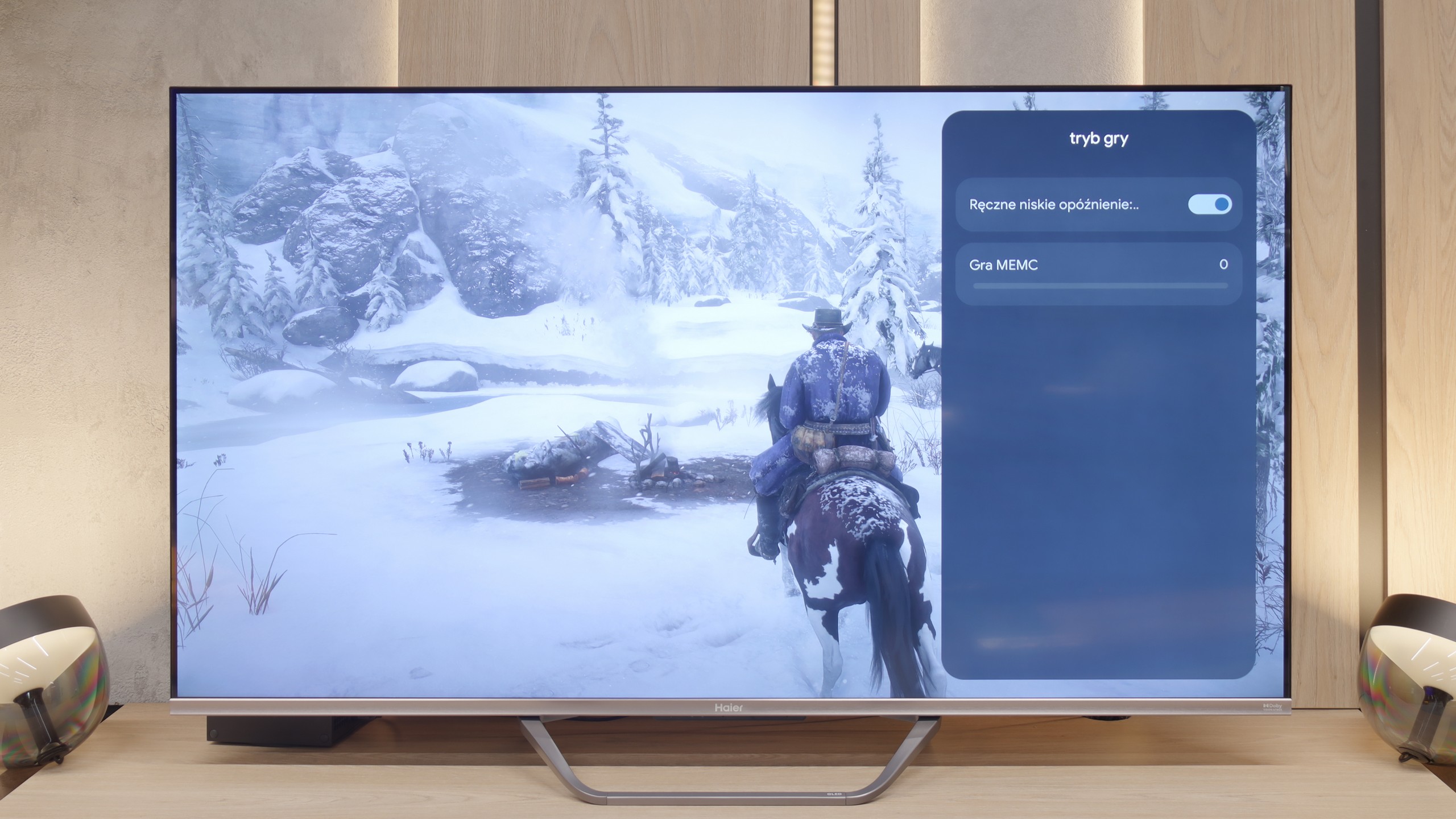


For gamers, the Philips MLED920 is truly a complete tool. The manufacturer has taken care of everything that is now considered standard in televisions for consoles and PCs. It has ALLM, so the console automatically switches the screen to game mode, there’s VRR and a 144 Hz refresh rate that ensures smooth gameplay even in fast-paced titles. All key HDR formats are supported – including HGiG and Dolby Vision Gaming for Xbox – which means that regardless of what you’re playing and on which console, the television will be able to extract the maximum potential from the image. In everyday gaming, the Game Bar proves useful too – a relatively simple implementation by Philips, but a functional panel where you can quickly check image parameters, enable VRR, or adjust details without leaving the game. It’s not as elaborate as the competition, but it does its job without any complaints. And finally, something that sets Philips apart from the competition – Ambilight. The three-sided LED backlighting can make a huge impression in games, especially in the evening. It’s also a way to slightly 'expand' the screen and create a greater sense of immersion. And since coloured LEDs have recently become almost an essential element of a gamer’s room, the MLED920 fits perfectly into this trend.
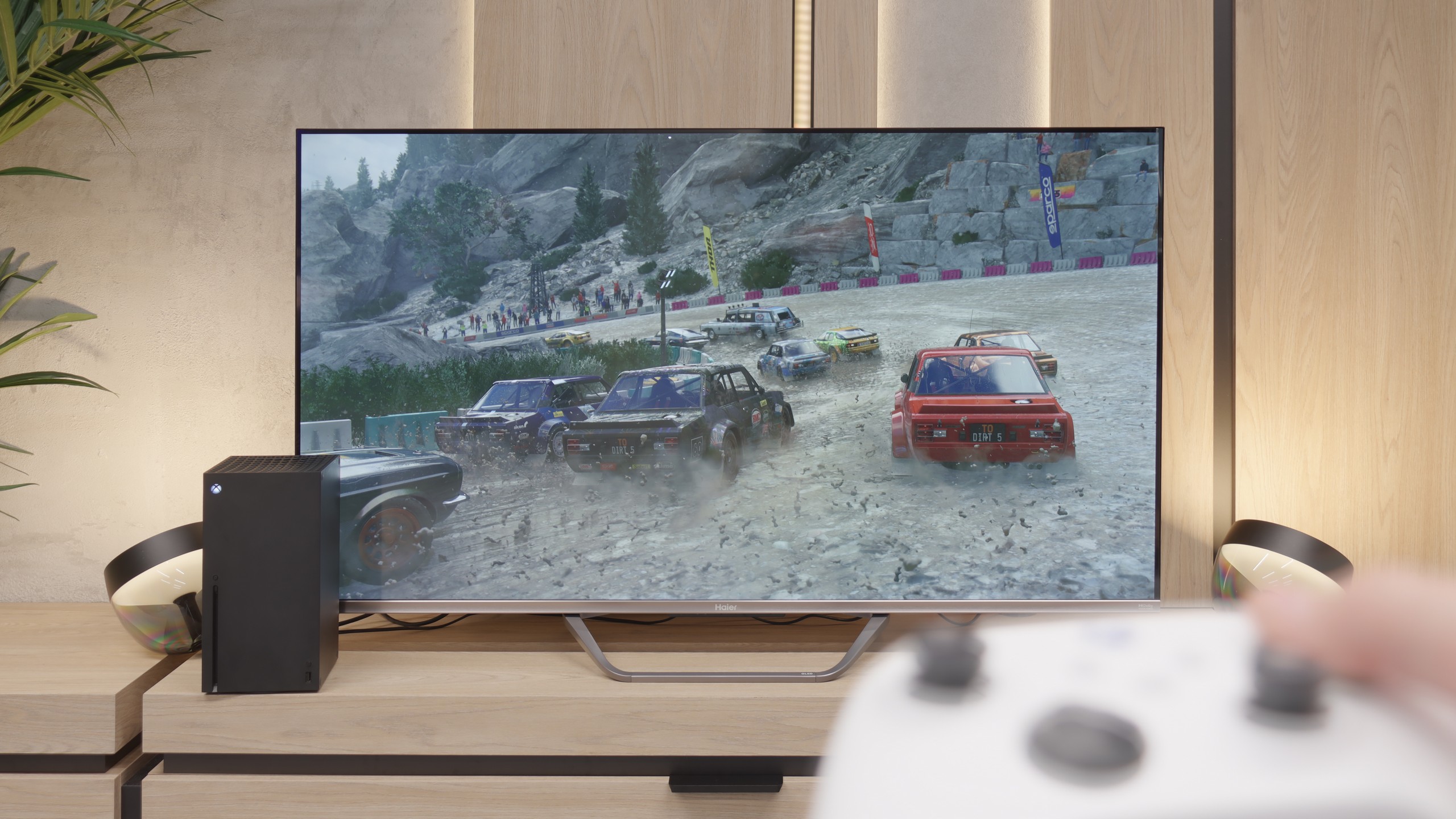
Entering the realm of gaming, the Haier Q80FUX proves to be quite a good companion for the "casual gamer." It is equipped with some highly sought-after features today such as VRR (variable refresh rate) and ALLM (automatic low latency mode). However, the biggest surprise is something else. Even though we don't have a 4K@120Hz panel here, the television can accept and display a 120Hz signal at a lower resolution (Full HD). This is a very useful feature, allowing you to consciously switch the console to a lower resolution mode in exchange for significantly higher fluidity, which is a perfectly acceptable compromise in the gaming world.
We won't particularly complain about the lack of additions like the "Game Bar," as it's just a nice extra. However, the most concerning issues arise when we enter the world of HDR in gaming. Due to the fact that the television continuously adapts the signal "in its own way," setting the brightness on the console according to the HGIG standard is almost impossible to accomplish according to the instructions. Worse still, in Dolby Vision mode for gaming, the input lag increases to around 50 ms, which is a high enough value that essentially makes this mode unusable. Generally speaking, we still wouldn't recommend gaming on this television in HDR mode, so these aren't that serious shortcomings. What’s most pleasing is the presence of 120Hz in Full HD, making the Q80FUX quite a cool television for the occasional gamer.
Input lag
9.6/10
9.4/10
SDR
HDR
Dolby Vision
The input lag on the Philips MLED920 is really very good – in 120 Hz mode, we measured values below 10 ms, which places this model among the absolute top of LCD TVs in terms of responsiveness. Even at 60 Hz, a result of around 18 ms is fully acceptable and won't interfere with any type of gameplay. One exception is the Dolby Vision mode at 60 frames, where the latency can increase to as much as 35 ms. This is a result that may be a bit glaring for esports players, but it must be stated honestly – for most so-called "casual gamers," it will be absolutely imperceptible. Especially since we're talking about values that still allow for comfortable gaming without major compromises.
If there is one category in which the Haier Q80FUX absolutely shines and shows its claws, it is input lag. In this respect, the TV presents downright outstanding results. In 120Hz mode (achieved, let's remember, at a lower resolution), input lag drops below 10 ms, which is an excellent value, worthy of top gaming monitors. Only slightly worse, but still at a very good level, is the classic 60Hz mode – here, measurements consistently indicated around 12-14 ms. These are results that much more expensive, dedicated gaming constructions would not be ashamed of. The only, but significant, stumbling block is the Dolby Vision mode. As we established earlier, its activation raises input lag to an unacceptable level, so we definitely advise against using it during any interactive gameplay.
Compatibility with PC
4/10
6/10


When it comes to working with a PC, the Philips MLED920 evokes quite mixed feelings. On one hand, it looks impressive on paper – we have 144 Hz, support for G-Sync and FreeSync, so in terms of gaming on PC, the TV does not disappoint. Anyone looking for a large screen for computer games gets a solid package of features here. However, when we try to use it as a typical monitor for everyday work, its limitations quickly become apparent. The fonts do not look the best – there is noticeable strong dithering, coloured letters can be jagged, and with very dark text, there are even strange anomalies, as if the panel is losing thin lines and having trouble reproducing them correctly. In short: For PC gaming, yes. For any work and reading text: a definite no.
We also checked how the Q80FUX performs when connected to a computer. Here again, we were pleasantly surprised – it handles this really well. The most important thing is that the fonts are very readable, so nothing blurs and you can work normally on it. Additionally, just like with consoles: we can set a lower resolution here to achieve a high refresh rate of 120Hz in return. What’s crucial is that in this mode, G-Sync started correctly and functioned well. This just confirms that this television is truly a successful and efficient piece of gear for gaming, also on a PC.
Viewing angles
3.2/10
3.3/10
The viewing angles on the MLED920 are classic for VA type panels – even a slight tilt from the centre causes the image to start losing colours, contrast weakens, and the overall picture becomes quite flat and less appealing. There are no miracles here. So if you’re watching films with a larger group and everyone is sitting a bit to the side, this will be slightly noticeable. On the other hand, you get what you pay for: thanks to this panel, the MLED920 can display a much deeper black than TVs with IPS panels.
Anyone planning screenings with a wide family group must be aware of the fundamental compromise that Haier has decided upon by implementing a VA panel in this model. This technology has indeed provided us with deep blacks and high contrast, but an inherent characteristic is also a noticeable narrowing of viewing angles. It’s enough to sit a bit further to the side of the couch to immediately notice how the colours start to lose saturation and the image fades. It’s simply a classic trade-off – we gain something (contrast) at the expense of something else (angles) – and the Q80FUX fits perfectly into this scheme.
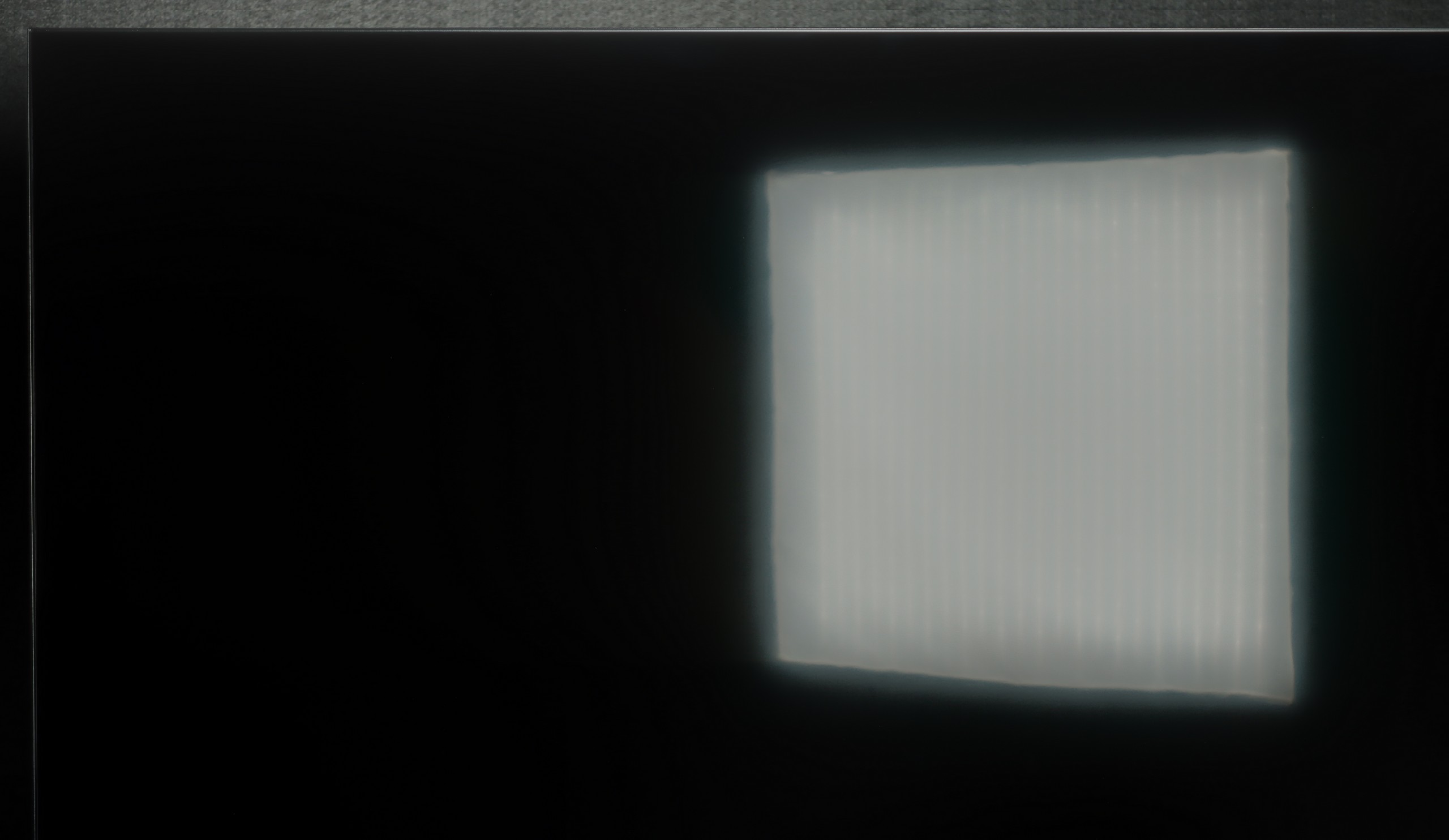
Daytime performance
5.5/10
4.8/10




Panel brightness
Average luminance SDR
Haier Q80FUX: 317 cd/m2
Philips MLED920 / MLED910: 421 cd/m2
Philips MLED920 performs quite well in everyday use. The satin finish on the panel effectively reduces reflections, and in most moderately sunny living rooms, it manages unwanted glare quite well. However, it's important to remember that this is not a TV that dazzles with brightness – the average value in SDR hovers around 450 nits. In very bright rooms, particularly with large south-facing windows, the screen doesn't always stand up to the intense daylight. In such situations, it's worth supporting it with even light curtains, so viewing comfort doesn't suffer too much.
The receiver's clash with the daily challenges posed by a bright lounge is quite decent with the Q80FUX, although it's certainly hard to talk about perfection here. The panel itself is equipped with a coating that effectively manages to suppress most reflections and glare from the surroundings. Equally important, even in more challenging lighting conditions, the screen can maintain pleasantly saturated colours. However, the weakness of this construction is revealed when backlight brightness comes into play. The previously mentioned, rather moderate maximum brightness (around 350 nits) means that in confrontation with intense natural light coming through the window, the screen often struggles to "break through." On a sunny day, the image might simply lack the necessary expressive strength.
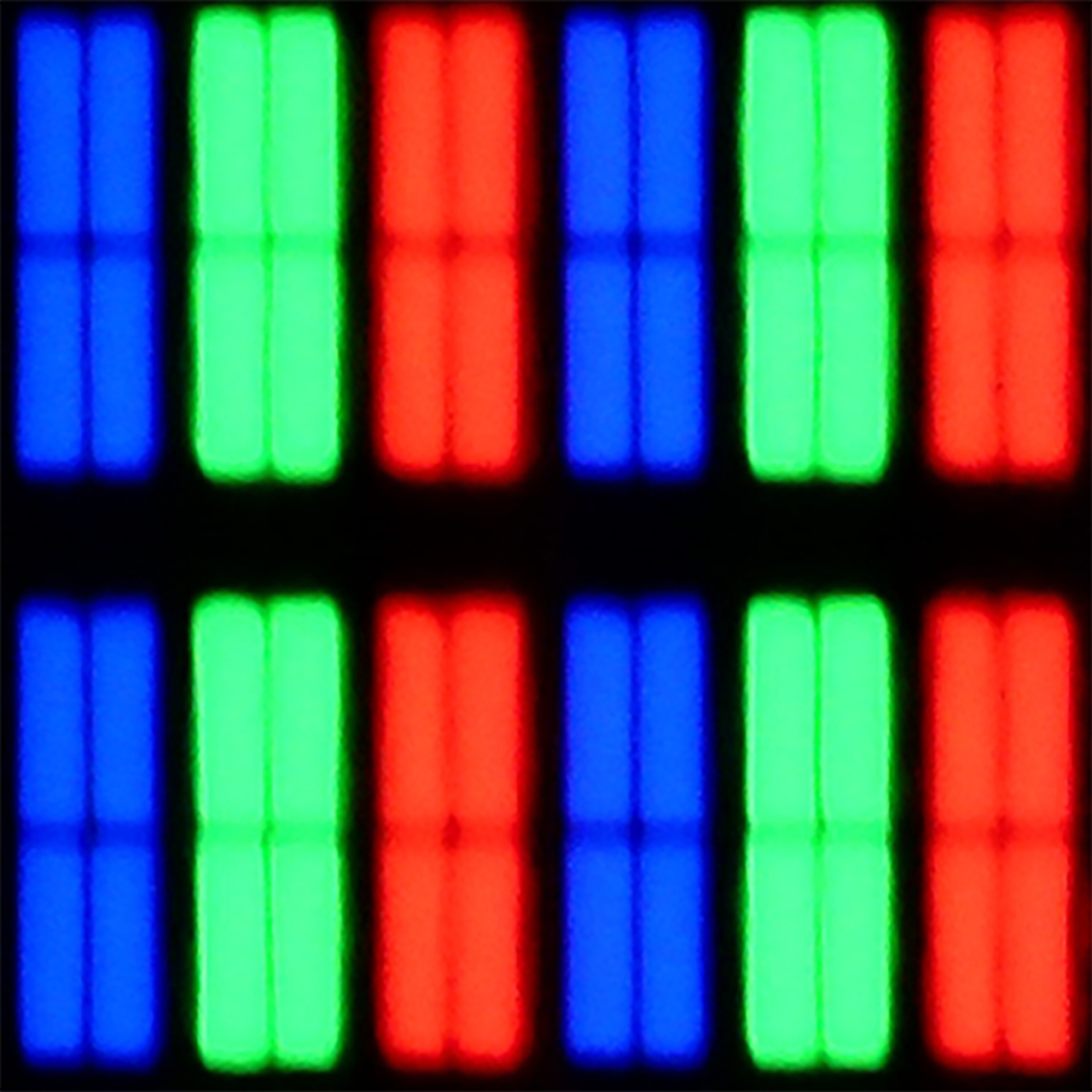
Panel details
Subpixel Structure:

Panel uniformity and thermal imaging:


Philips MLED920 / MLED910
Haier Q80FUX
TV features
5.5/10
5.6/10
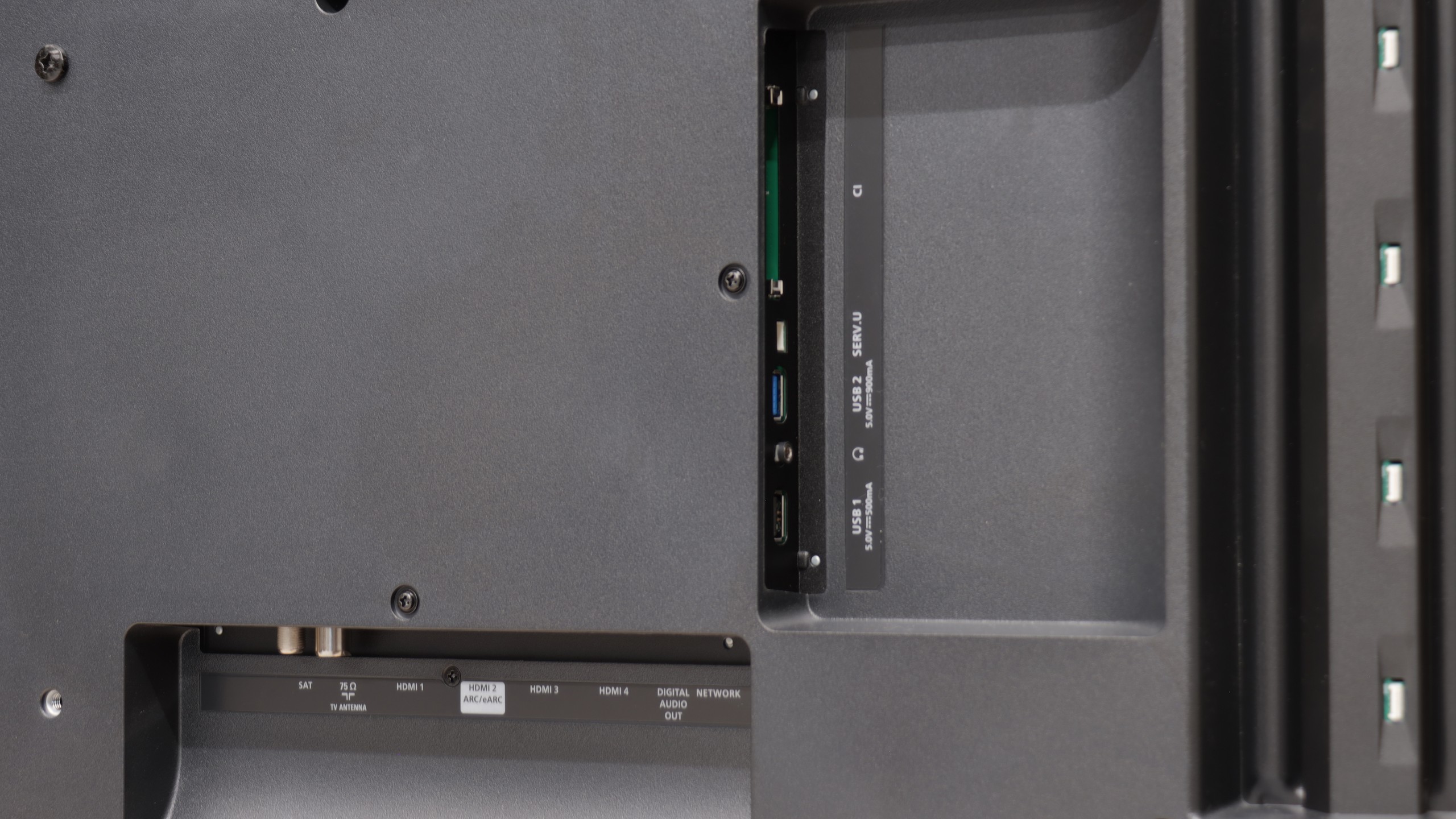
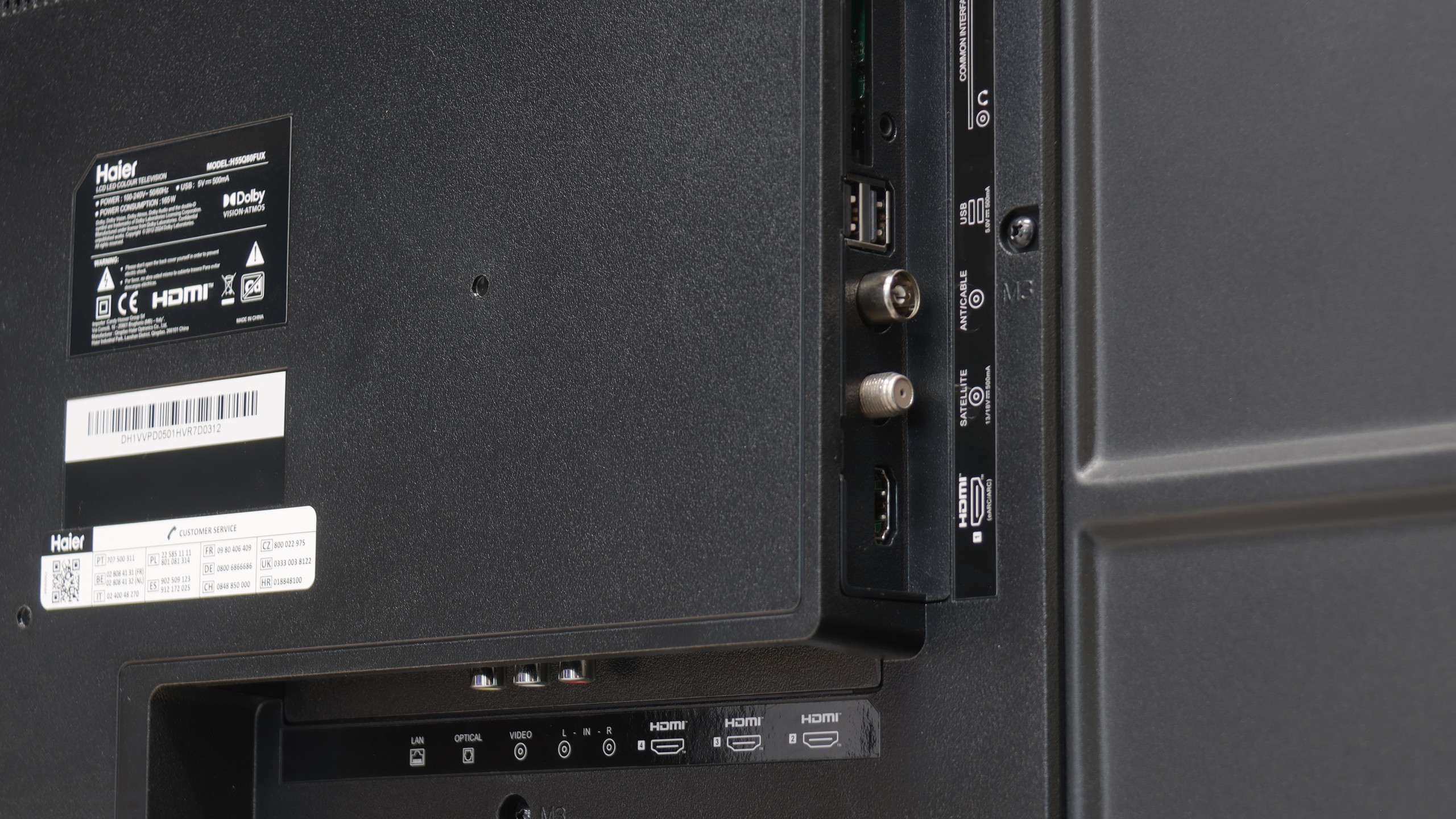
- HDMI inputs0 x HDMI 2.0, 4 x HDMI 2.1 48Gbps4 x HDMI 2.0, 0 x HDMI 2.1
- Other inputsRCA (Chinch)
- OutputsToslink (Optical audio), eARC (HDMI), ARC (HDMI), Mini-Jack (Headphones)Toslink (Optical audio), eARC (HDMI), ARC (HDMI), Mini-Jack (Headphones)
- Network InterfacesWi-Fi 2.4GHz, Wi-Fi 5GHz, Ethernet (LAN) 100MbpsWi-Fi 2.4GHz, Wi-Fi 5GHz, Ethernet (LAN) 100Mbps
- TV receptionDVB-T, DVB-T2, DVB-S, DVB-S2, DVB-CDVB-T, DVB-T2, DVB-S, DVB-S2, DVB-C
Classic features:
- Recording to USB (terrestrial TV)
- Recording programming
- Picture in Picture (PiP)
- RF remote control (no need to aim at the screen)
- Backlit remote control
- Teletext
- Audio only mode
- Bluetooth headphones support
- Simultaneous Bluetooth headphones & TV audio
Smart features:
- AirPlay
- Screen mirroring (Windows Miracast)
- Voice search
- Voice search in native language
- Ability to connect a keyboard and mouse





Smart TV – Titan OS
Philips MLED920 uses the proprietary Titan OS, which is just starting its adventure in the TV market and unfortunately, this is evident at every turn. On one hand, we have basic features – such as AirPlay support or the ability to mirror content from a smartphone, but on the other hand, its limitations quickly become apparent. Screen mirroring works only with a phone, but not with a laptop. Voice search? Yes, but it only works with Amazon Alexa and in languages supported by this assistant. The system operates fairly quickly, but every now and then it can "fail" and gives the impression of something that is underdeveloped and still evolving.
Classic TV Functions
Titan OS also doesn't excel in terms of classic TV functions. Aside from the hybrid remote with a numeric keypad – which is indeed backlit and thoughtfully designed in two modes, it unfortunately operates on infrared – there’s nothing here that would truly set the MLED920 apart from the competition. There’s a lack of USB recording or a PiP function, and such solutions could be useful in this class. From unusual additions, we have an analog output in the form of a jack, which allows for connecting headphones or older speakers. It’s a small nod to users who still use older equipment.
Ambilight TV
What definitely draws attention away from the shortcomings of Titan OS is the unique, three-sided Ambilight system. Here, Philips still plays in its own league and can impress those who haven't experienced this feature before. The colour backlighting that reacts to the content on the screen adds a unique atmosphere to viewing sessions and is something that the competition does not offer in a similar form. It is precisely Ambilight that is meant to ensure that other shortcomings – both system-related and functional – take a back seat.
SmartTV on Haier Q80FUX: GoogleTV
First up, let's take a look at the smart layer, which in the Q80FUX is managed by the Google TV system. This is theoretically a huge advantage, providing access to an incredible library of apps, making it easy to cast from mobile devices, and offering convenient voice search. Unfortunately, like in other models from this brand that we've tested, the implementation of this platform leaves much to be desired. It’s not even about drastic freezes or delays in navigation, but rather a festival of minor bugs, shortcomings, and terrible translations in the menu. Because of this, it's hard to consider "Google TV" in Haier's version on par with what we know from Sony or TCL receivers, even though the same, proudly sounding name is on the box.
Classic Features
Moving on to the classic, functional features of the TV, the device's performance does not improve at all. The only thing worth praising is the presence of Bluetooth connectivity and an unusual but handy relic of the past in the form of an analogue headphone jack output. Apart from that, it's hard to find anything that would excite us. Due to the problematic software, the receiver (like its predecessors in our tests) was unable to find any terrestrial TV channels, even though other TVs connected to the same installation had no such issues. The remote control is also strange – its design may appeal to some, but due to the lack of a numeric keypad and the absurd placement of some buttons on the side edge, it definitely cannot be called senior-friendly.
Playing files from USB
8.5/10
9.6/10
Supported photo formats:
Maximum photo resolution:
The built-in player in the Philips MLED920 works quite well and handles most popular audio and video files without any major issues – just as you can see in our test table. So there’s no worry about typical movie or music formats. The only complaint we can have is regarding its rather selective support for photo formats and some resolutions.
We must admit that after a series of setbacks we faced in assessing the overall implementation of the Google TV system, we approached the media player test with a fair bit of caution. Meanwhile, in this one specific aspect, the Q80FUX served us a real surprise. The built-in app for handling files from USB drives works simply brilliantly. This software component seems to be completely immune to the issues plaguing the rest of the system, opening practically all the most important and popular video file formats that we threw at it.
Apps
6.7/10
9.6/10










































Sound
6.2/10
5.5/10
- Maximum volume88dB84dB
- Dolby Digital Plus 7.1
- Dolby True HD 7.1
- Dolby Atmos in Dolby Digital Plus (JOC)
- Dolby Atmos in Dolby True HD
- DTS:X in DTS-HD MA
- DTS-HD Master Audio
The sound in the Philips MLED920 is probably not the element that will impress you the most. It sounds fairly flat, lacking depth and clearer bass, which means movies or concerts don't have that extra layer of immersion that a better audio system can provide. However, it must be said that the volume is at a really decent level – the TV can ramp up to even 88 decibels. A big plus of the MLED920 is not so much the sound quality itself, but the support for audio formats. Philips has ensured compatibility with virtually all the major standards, including Dolby Atmos, DTS, and Dolby TrueHD 7.1. This means that if someone decides to connect an external soundbar or amplifier, they won't encounter any limitations and will be able to enjoy the full cinema sound.
When it comes to "acoustic experiences," the Haier Q80FUX seems to adhere to the principle that sound is simply meant to be. And it is – that's about all that can be said for it. The built-in speakers produce sound in an extremely flat manner, lacking character, and most importantly, they are missing any clear bass foundation. A slight consolation is the fact that the television supports the Dolby Atmos format. However, let's be honest: to realistically take advantage of the benefits of this codec and hear the promised space, passive decoding capability is simply not enough. Connecting an external home theatre system or at least a decent soundbar is not just a recommendation in this case; it's an absolute necessity.
Sound Quality Test
Acoustic Measurements
88dBC (Max)
75dBC
84dBC (Max)
75dBC
